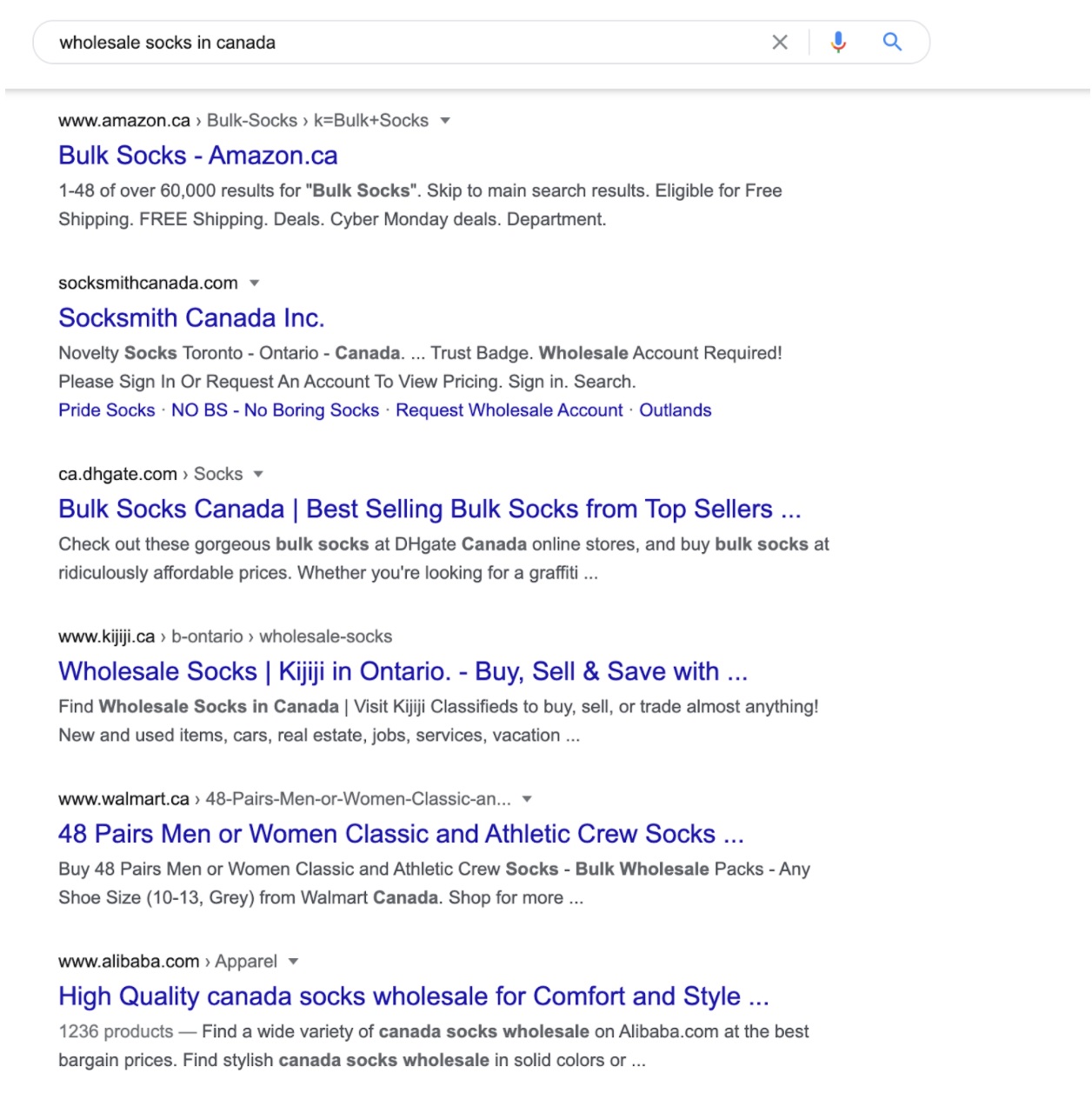
Building an e-commerce site has taken you months, maybe years. I’m still not seeing any movement. Check out our e-commerce SEO strategy to get more visitors to your site.
In order to attract new clients, it might be difficult to be found by search engines. You need customers for your e-commerce site to be successful. (It’s obvious, isn’t it?). The difficulty is that attracting clients’ attention is pricey.
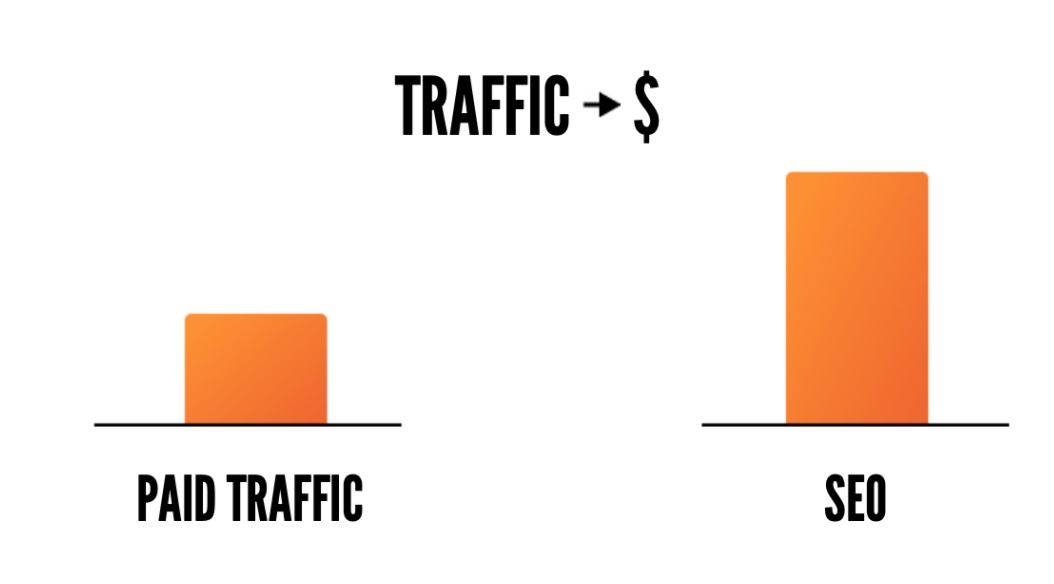
Just a few new customers might cost you thousands of dollars. With SEO, you may help your site rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) and get free (yes, free!) organic traffic.
Why eCommerce need SEO ?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is a powerful tool that has helped many people build an online presence on Google. Now they’re just maintaining it and getting organic (=free*) traffic from search engines.
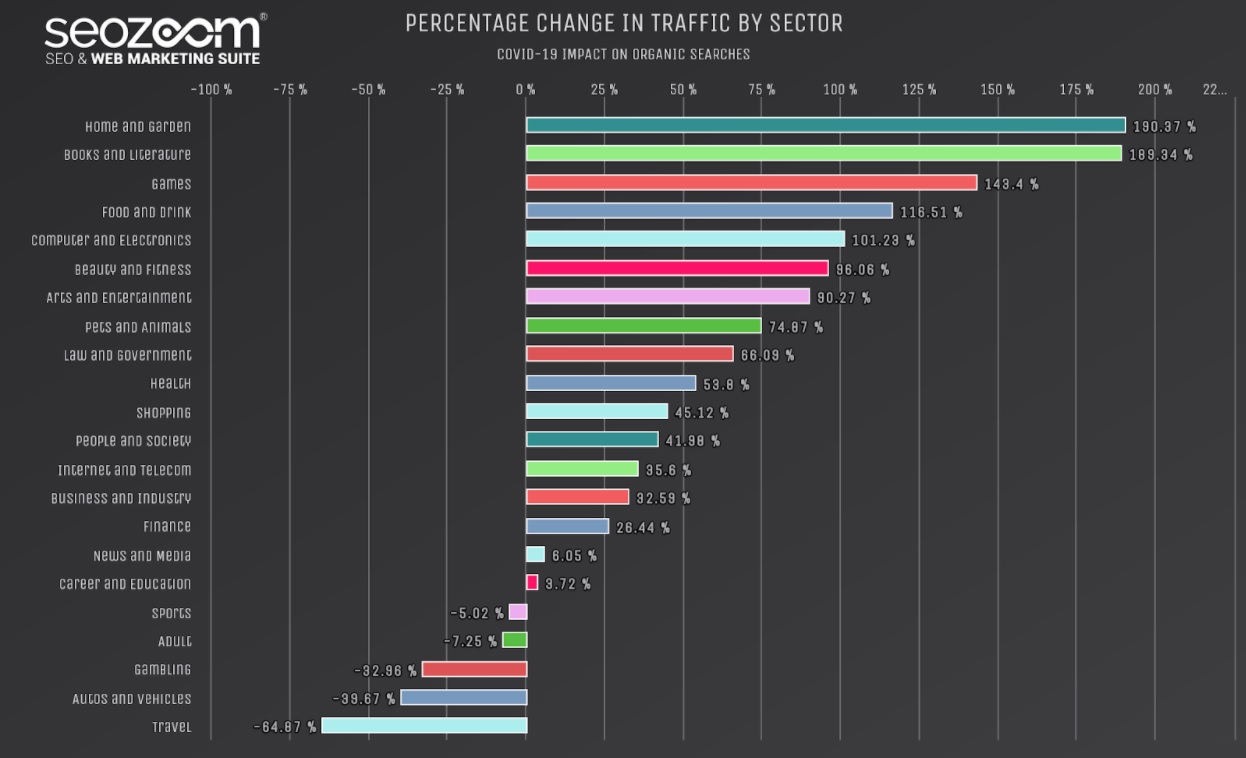
Let’s take COVID as an extreme example that has caused a sudden shift in user behaviour: people switched from offline shopping to shopping for products online. It means many sectors have seen a much higher demand.
Here’s a breakdown of traffic by sectors:
SEO is ‘free’ traffic because you don’t need to pay for each click or impression your website gets.SEO services are not free
The stores which were investing in their visibility on Google have seen a massive increase in sales. At the same time, those who didn’t invest in SEO had to spend more money on ads (or disable ads to cut the budgets, resulting in decreasing sales).
So here’s why SEO is the answer
-
With SEO, you get traffic consistently
Even when you sleep, even when you’re enjoying the sun sitting on a cliff surrounded by a beautiful forest. Always.
-
SEO is scalable
Imagine yourself a year from now. If you start search optimization today, in a year, you will have a strong channel bringing people to your website (though you’ll see the first results much faster).
If you put money and efforts only in the paid channels instead (e.g. Google Ads, Facebook Ads), nothing will change in a year: once you disable your campaigns, all traffic will be cut off.
-
High conversion rate
People who specifically look on Google for the products you or your client offer and find them there will most likely buy from you. The conversion rate of free Google traffic is higher than paid or other traffic types.
1. Optimize Product and Category Pages
Most of the time there are many ecommerce site has just the title tags on their category pages say something vague and general, e.g. ‘Plates’.
Here’s the truth: The Title tag and H1 tags should be specific to the page content. If you’re an SEO, you know exactly what this mean.
What is the Title tag?
The title tag, which is an HTML tag nested within the <head> of the website, and is found within the <title> HTML tag. It is one of the best indicators to search engines on a page’s content; it is an important ranking factor.
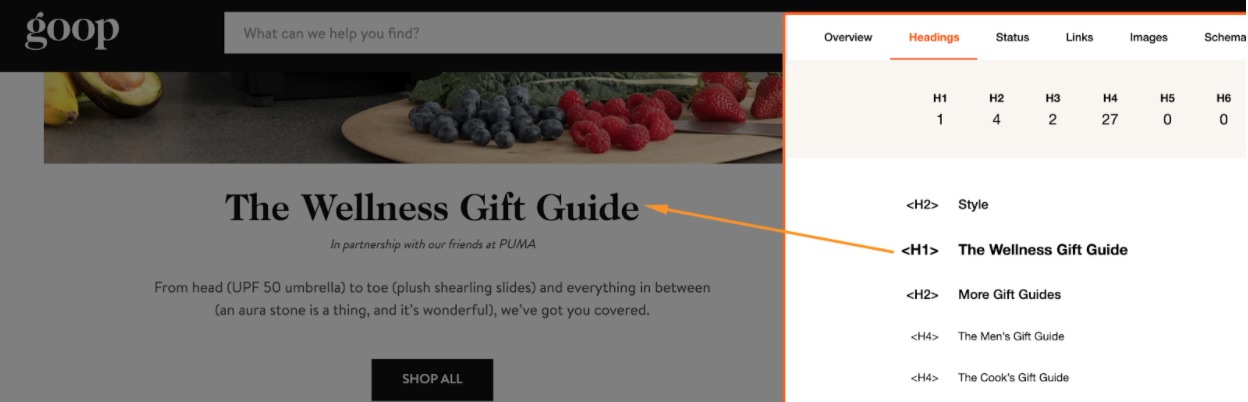
The title also affects click-through rate from the Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) by acting as the sales copy. You can see the title tag in the search results – it’s shown to users in search results as the most visible element of your search result:
The Title tag is also seen in the tab name:
What is the H1 tag?
The H1 tag is an HTML tag that exists anywhere in the <body> section of a web page within the <h1> HTML tag and generally appears to the user as the visible title of the page. The H1 tag is another significant indicator to search engines on the content of a page.
Why Title and H1 tags are important ?
The Title and H1 tags show what your page is about. It’s what you’re trying to rank for. So every time you see a Title tag (or H1), ask yourself: is that what I’m trying to rank this page for?
With that logic, ‘Plates’ (as in the example above) is not a good title tag, ‘Beautiful Dinner Plates in Canada’ sounds much better.
How to Optimize Title and H1 tags ( Product and Category Pages ) ?
we’d recommend starting with category pages since they usually get more traffic than the product pages. The good thing is that the approach to optimizing the category pages that we will cover below will work for product pages as well.
Step 1. Define specific information that should be added to the Title and H1 tags
- General characteristics of the online store applicable to all products (e.g. ‘personalized’, ‘custom’, ‘wholesale’, etc.)
- Specific characteristics applicable to this product/category (e.g. ‘bandage’ for dresses, ‘christmas’ for gifts, etc.)
- Product characteristics (e.g. size, color, type, brand, etc.)
- Target audience (e.g. for boys, teens, women, etc.)
- Location (e.g. Canada, Toronto, New York, etc.)
Our advice is to go through each of these pointers and choose those relevant for your or your client’s online store.
Let’s pretend this is the title tag you have now: ‘Gifts – Brand Name’ After going through the pointers above, this Title tag can become something like this: ‘Personalized Gifts for Her in Toronto – Brand Name’ Now it looks much better, right? It’s optimized.
Step 2. Use templates for the Title tags and H1s to streamline the optimization process
To make the optimization process faster, define the title tag templates for your category and product pages. These templates will include the pointers from the first step.
A template for a category can look like this:
Personalized {Category Name} in New York with Free Shipping – Brand Name
e.g. Personalized Gold Necklaces in New York with Free Shipping – Zola
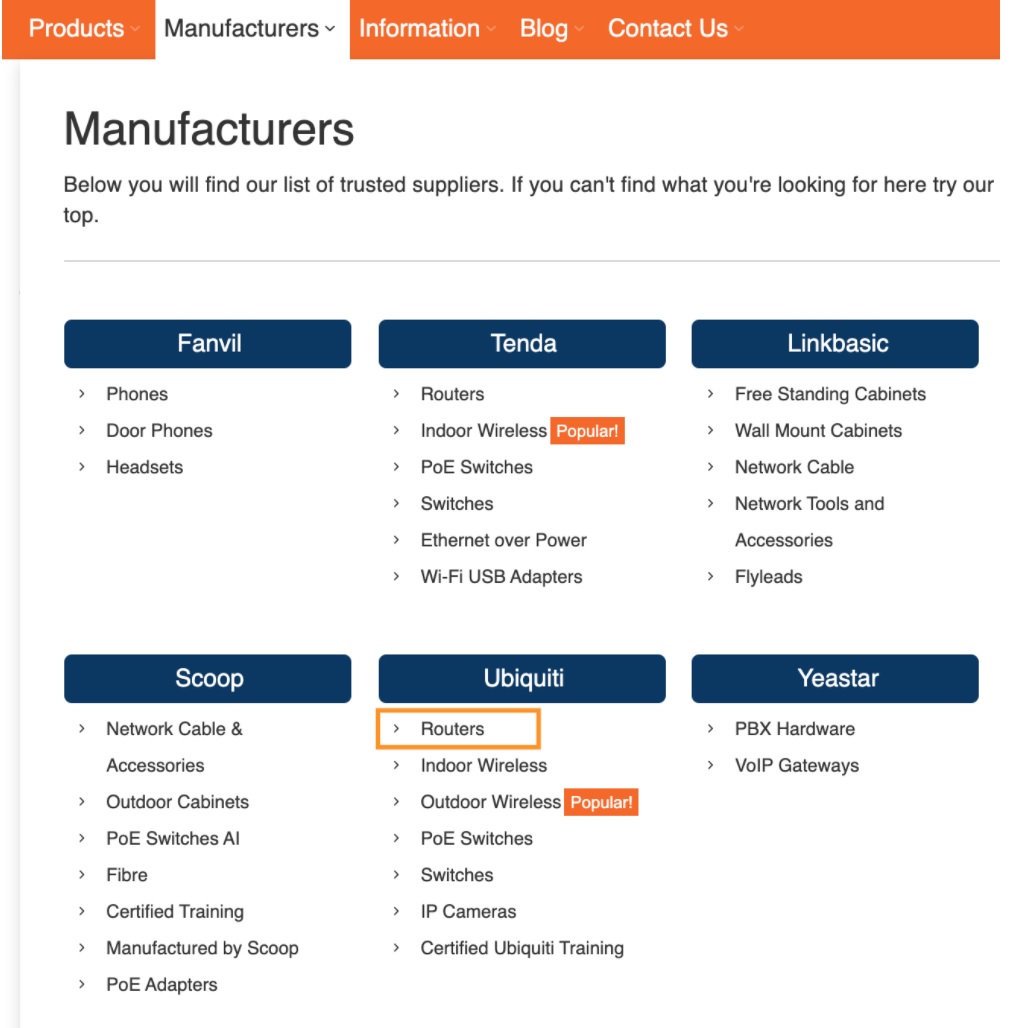
The H1 tags will follow the same template except for the ‘Brand Name’ at the end, you don’t need to include it. Make sure that your navigational links anchors and H1 tags are not mutually dependable!
For example, you can have ‘Routers’ as the navigational link anchor:
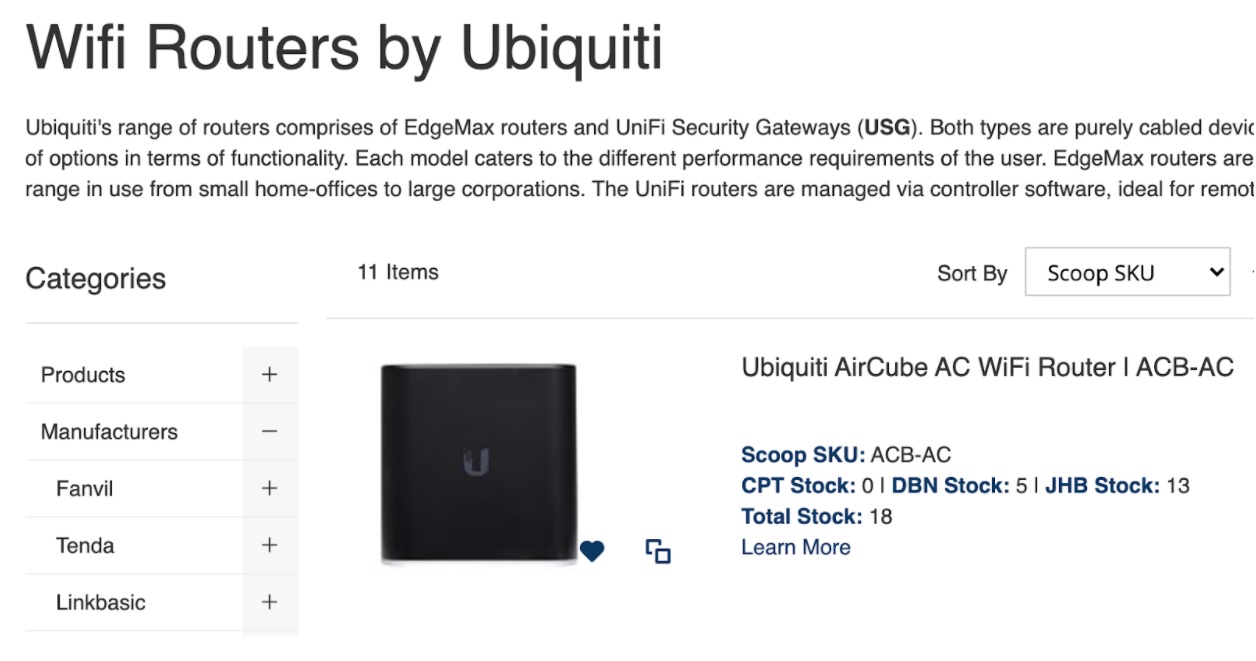
and ‘Wifi Routers by Ubiquiti’ as the H1 tag:
Step 3. Customize individual Title Tags if needed
Using tag templates is great as they help you optimize the pages fast. The downside is that when using an automated approach like this, you can’t customize Titles or H1s for individual pages.
That’s why once the templates are done, you can now dig deeper and customize the title tags and H1s on the individual pages based on the keywords you need to use.
Step 4. Add a unique copy to the category pages
This is the most challenging part since it might not be easy to come up with a unique copy for each category. That’s why it’s the last step in the optimization process.
Steps 1-3 might be enough depending on the competition. If they’re not, add 100-200 words of copy at the top of your category pages, for example:
2. Create Specific Product Categories Instead of Broad Ones
Being specific is what helps to attract the right people and also face a lower competition in the search results. Think about it: when you’re looking for concert tickets, you don’t want any tickets to any concert, right? You want particular tickets, e.g. an Adele concert.
So you expect to see them as a separate offer, not somewhere buried on a single page listing all upcoming shows. The same logic applies to an online store. It should provide solutions for specific needs its customers have.
If it sells just ‘jeans’ and ‘t-shirts’, this is too general. Having categories for more specific items like ‘skinny jeans’, ‘skinny jeans for men’, ‘v-neck t-shirts’, ‘sleeveless t-shirts’ is a much better strategy.
The problem we see too often is that online stores concentrate only on general product types like ‘jeans’ and ‘t-shirts’ rather than going deeper and capturing long-tail searches
Why Specific Product Categories are important ?
When you have too general categories, you:
- Face tough competition and are ‘killed’ by larger stores
- Don’t meet specific users’ needs
Having narrow categories targeting long-tail keywords solves this issue
How to Optimize Product Categories
You don’t want to create new categories just for the sake of creating them, right? That’s why you’ll need a solid approach. Find it below.
Step 1. Come up with ideas for new categories
You should look at your customers’ needs from different angles. That’s why you’ll need to use several different sources. Group your existing products in a new way using the TOP framework.
This framework will work for any kind of online store. Small and medium stores can go through it manually, while bigger stores can streamline this process.
The goal of the TOP framework is to help you look at the store products from a different angle. Think about the following characteristics:
- Target audience – who are these products for? It can include either the audience who buys the items or the audience who will be the end-user.
- Occasions – when can these products be relevant?
- Product attributes – such things as color, size, etc.
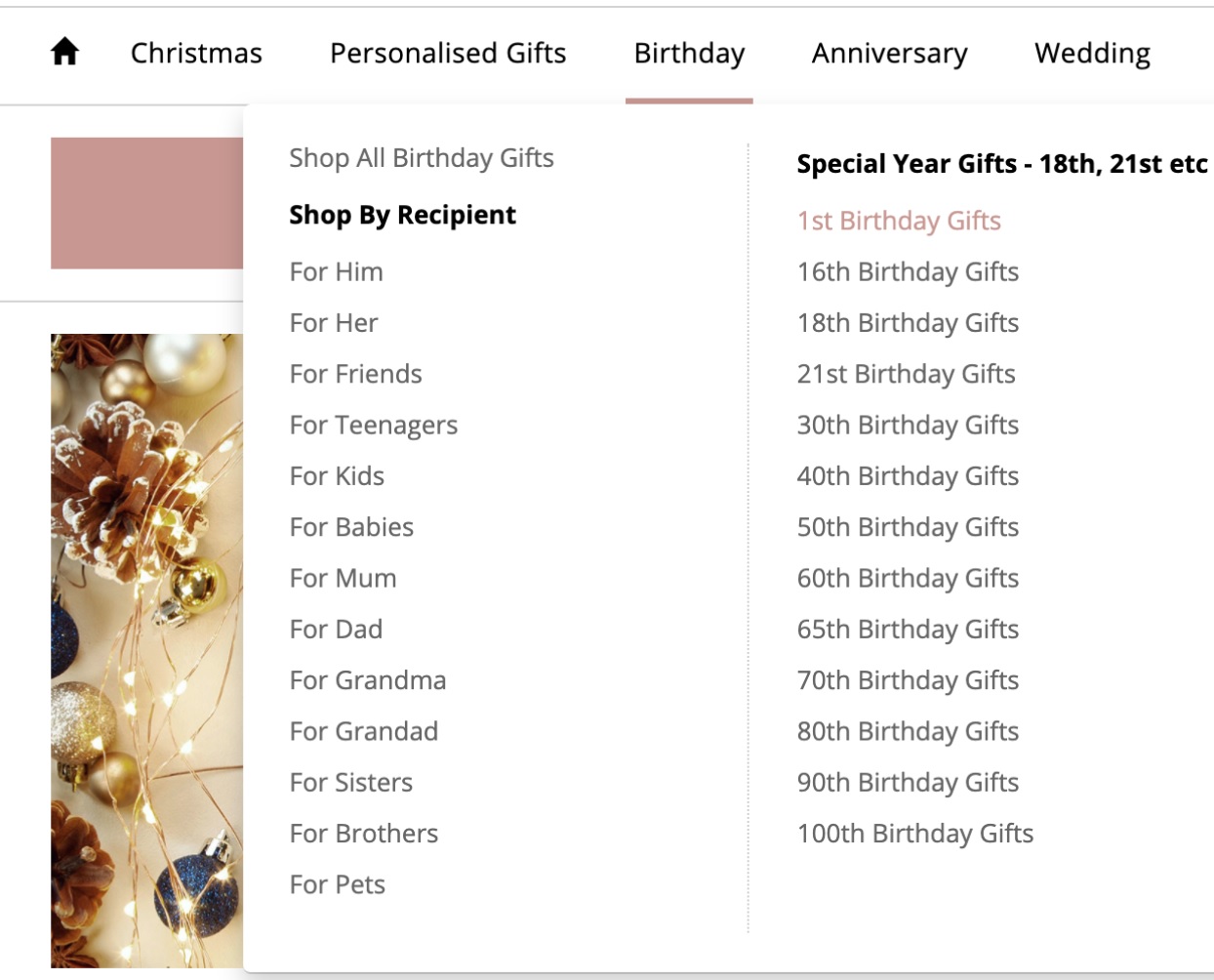
For example, an online store selling baby gifts can have the following additional categories:
- Baby gifts for boys (target audience, end-user)
- 1st birthday gifts (occasion)
- Pink baby gifts (color)
Analyze your internal site search
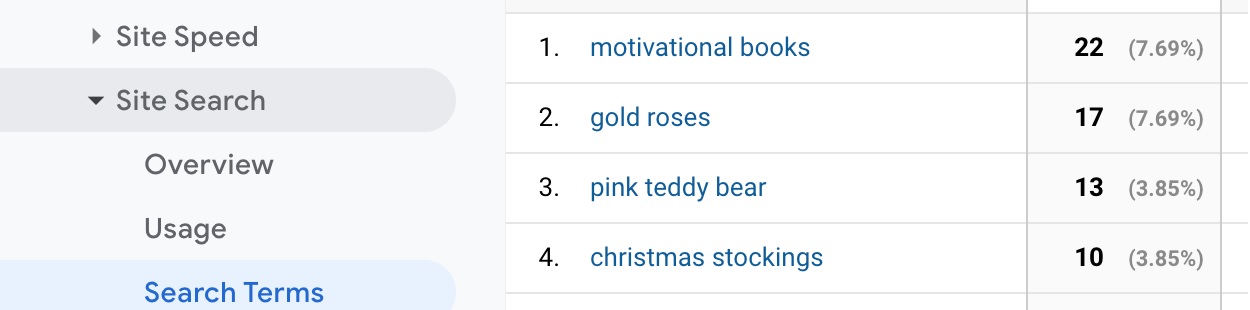
Your internal site search can shed light on what your customers were looking for on your website but couldn’t easily find (because if they could, they would not use the search bar, right?). You can find very interesting data hidden in your search terms in Google Analytics:
If you don’t see the Search Terms for your store in GA, it might not be configured yet. we highly recommend setting it up, The search terms can provide you with valuable insights into which categories you can create in your or your client’s online store.
By the way, eBay gets it right when it comes to the internal search: they have an automatic system that monitors it. And if many people start looking for particular items, the system automatically creates a new indexable product category page that is then linked from other internal pages.
Of course, developing such a system is expensive. But let’s be honest, not all stores have as much traffic and data as eBay. So performing an internal site search analysis manually or using Google Sheets, etc., will work perfectly.
Explore Google Image Search
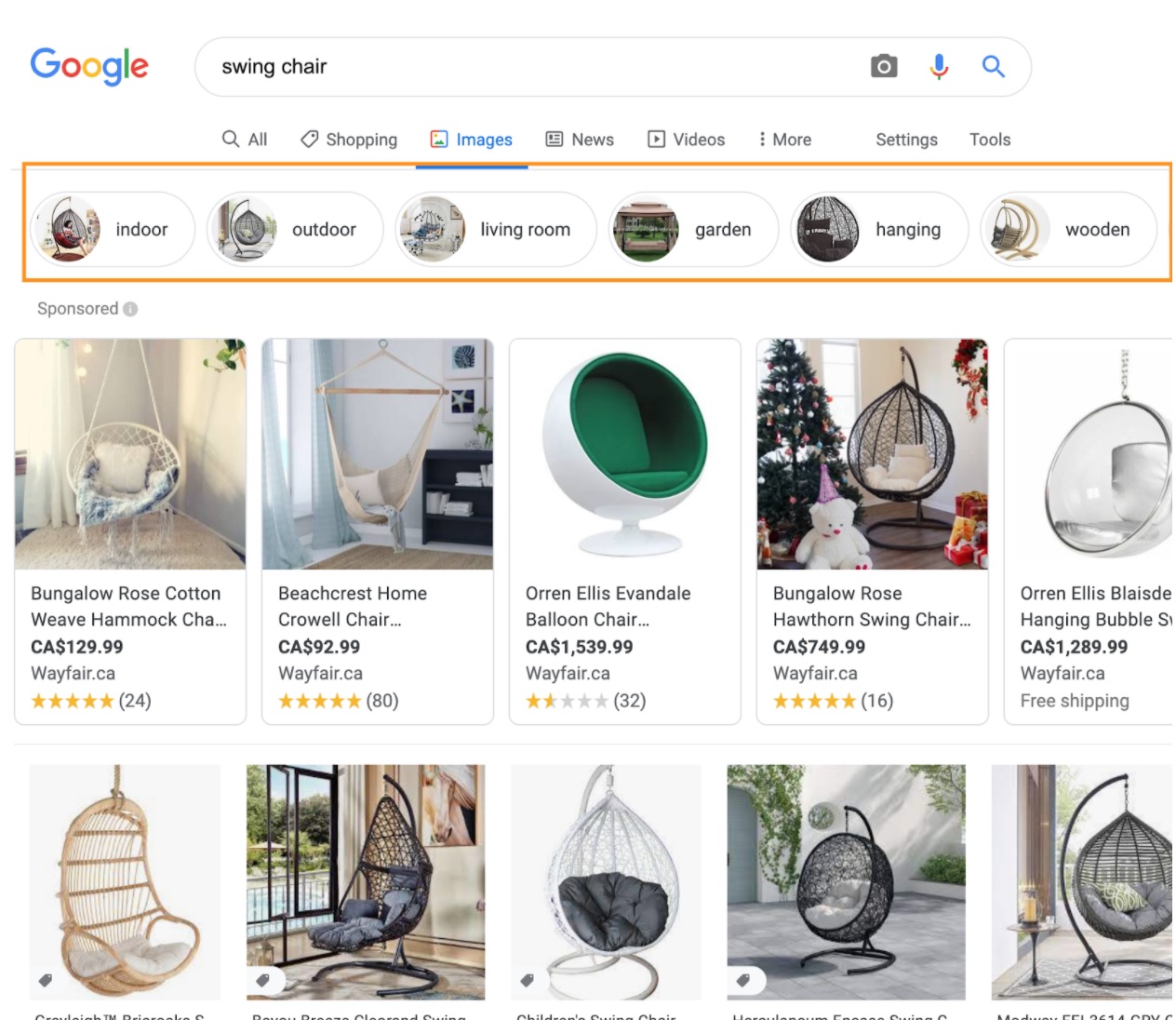
One of the best tricks to use is looking at Google Image Search. It’s very handy as it groups different types of products based on some characteristics they have. Just look for a product and see how Google groups this product into different types.
we’ll use [swing chair] as an example:
This search would give these great ideas:
- Indoor swing chair
- Garden swing chair
- Wooden swing chair
- Etc.
This info comes directly from Google and is based on popular searches. So it’s definitely worth checking out
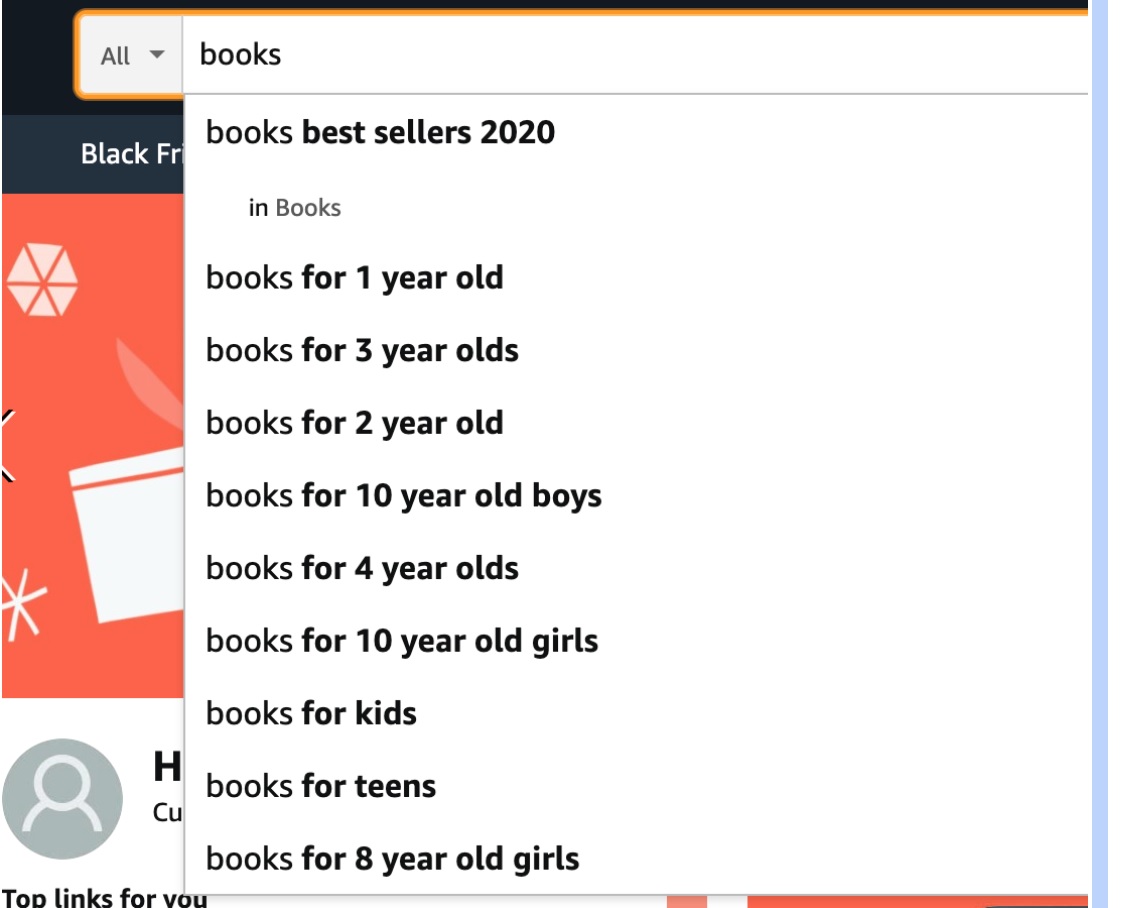
Look at Amazon search autosuggest
Amazon has a massive database of search terms. It uses this database to help customers find what they came for much faster. And we’ll use Amazon search to get ideas for product categories.
Just go to Amazon and look for the main keyword related to the products that your or your clients’ online store sells. For example, [books]:
As you can see, there are plenty of ideas to go through. In this case, most of them are connected with the target audience (from the TOP framework we shared above).
Step 2. Complete keyword research to see customer demand
Once you’ve completed the first step, you will have a list of specific product category ideas that you can target. But before creating them, you need to make sure that they will work for your or your client’s online store.
So you need to go through this second step – keyword research. It will also help you prioritize creating the new categories as you will start with those having a higher search demand.
we won’t go into details on specific keyword research tools here. There are so many of them, you can choose any you like.
You’ll need to take the ideas of new product categories you got from Step 1 and run them through your keyword research process to check if there’s enough demand for that. In this step, you might also find new ideas.
Step 3. Create category pages based on your keyword research
Now you have product category ideas and keyword research completed for them. so keep in mind that there are many things that you need to get it right for this. therefore we will discuss them here.
How to prioritize the categories creation?
- Start with those that have the highest demand (more monthly search volume)
- Add these categories across all relevant product types. For example, if I add a category for ‘Baby gifts for girls’, I’ll add ‘Baby gifts for boys’ as well since they are of the same type (even though ‘Baby gifts for boys’ might have low search volume). I’d call this approach symmetrical.
- Prioritize seasonal content when relevant. For example, if Christmas is coming, I will prioritize Christmas-related categories over other ideas.
How to prioritize the categories creation?
It greatly depends on the demand in your niche in general. If most of the categories have keywords with MSV (monthly search volume) of 300+ searches per month, you might skip category ideas with just 10 searches per month.
But if the overall search volume in your industry is not that high, the ‘10-searches/month’ keywords are worth attention for sure. because they can bring in lots of $$$.
What if a new category will have just 1-3 products?
Don’t create such a category then. At the end of the day, we as SEOs need to create a better user experience. A page with just a few products will most likely not rank anyway.
Have a threshold of products that will need to be met if you create a new category. It can be 6, 9, or 12 items per category.
Step 4. Optimize the new pages
This step is essential, so see ‘Win 1: (Really) Optimize Product and Category Pages’ in this guide.
Step 5. Link to the new pages internally
Internal links are often overlooked while people are chasing external links (aka link-building). But internal links are very important.
- They Help users navigate through the website easily.
- Help Google discover and index the new pages easier.
- Transfer ‘authority’ from other internal website pages.
The main areas where you’d need to add the links to your new categories are:
- The main navigation (if you don’t have too many links there already)
- In the content blocks on the homepage and other category pages
- Breadcrumbs on the category and product pages
Real-life example
Followed website had categories like Bras, Panties, Shapewear. All they made sense, but they were too broad. Based on the keyword and competitor research, you can come up with more specific subcategories: Sports Bras, Bralettes, Strapless Brass, etc.
Some of these pages were further broken down into sizes (if there was a substantial demand for that). These changes helped bring more people looking for specific types of products and ready to buy them:
3. Duplicate Category Pages to Consolidate Value
Let’s say you have a category listing women’s t-shirts. But there are 2 ways how people can find this category
Both ‘Women’s T-shirts’ categories list the same products, but their URLs might be different
Why Duplicate Category Pages are important ?
As we started to talk about t-shirts, let’s use them for another example! Think about your favourite t-shirt (or dress or suit, it doesn’t matter!). You like it because it’s special for you. Maybe you like the print or the texture or the emotions associated with it.
Remember how you feel wearing it. Now imagine that in addition to this t-shirt you bought 10 more exactly the same ones. Firstly, it doesn’t really make sense. Secondly, the value of the t-shirt has significantly decreased. Which one is better? Which one should you wear today? Now it’s much harder to decide when you have multiple identical t-shirts!
The same happens to Google when it sees multiple categories with the same products in your store. The value of each page decreases. Which one should Google choose to show?
Though Google is a giant with massive resources, it won’t waste them hand-picking the right category variation
How to Optimize Duplicate Category Pages ?
Imagine you could tell Google ‘Ok, here’s my Page A, Page B and Page C, which look the same. So I want you to take into account and rank only Page A.
But I don’t want to lose any authority or people or links coming to Pages B and C, so I need you, Google, to transfer all of it to Page A too’. That’s basically what you tell Google with a canonical tag. A canonical tag is placed in the <head> section of your page.
Here’s how a canonical tag looks like:
- Page A – a canonical tag pointing to ?
- Page B – a canonical tag pointing to ?
- Page C – a canonical tag pointing to ?
The Answer:
- Page A – a canonical tag pointing to Page A
- Page B – a canonical tag pointing to Page A
- Page C – a canonical tag pointing to Page A
By adding canonical tags pointing to Page A, we ask Google to ‘glue’ these pages together and use Page A as the main one. Google also calls it ‘deduplication
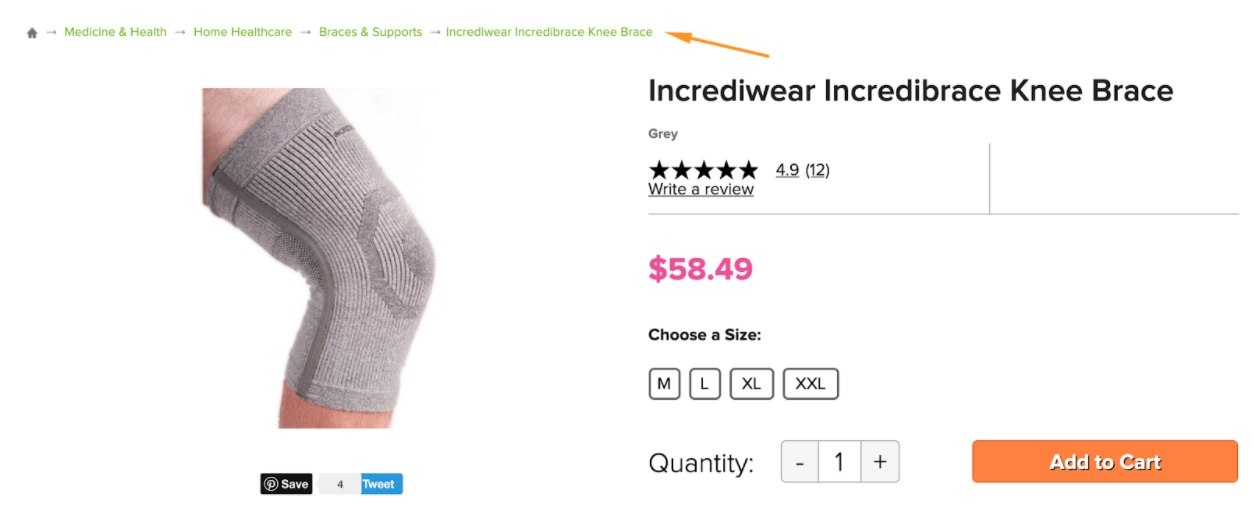
4. SEO-Friendly Product Variations
After you learned about the duplicate categories, it will be much easier to understand the mistake of having too many similar products.
Examples,
- Orange polka dots dress
- Pink polka dots dress
- Green polka dots dress
- Purple polka dots dress
- Yellow polka dots dress
Now imagine all of these dresses are 100% the same. The only differentiator is their colour.
Why Product Variations are important ?
When you have the same product details and photos on multiple pages, you don’t create any additional value. Remember the example about the same t-shirts we talked about above? Now the t-shirts are not 100% the same; they have a different colour.
But in most cases, just colour is not enough to make the individual page stand out (of course, there are rare exceptions). If people don’t specifically look for [purple polka dots dress] but look for [polka dots dress] instead, what page should Google show? Should it be a green dress? Yellow one? Orange? Confusing, right?
That’s confusing for Google too, and it just doesn’t bother to show any of the pages.
How to Optimize Product Variations ?
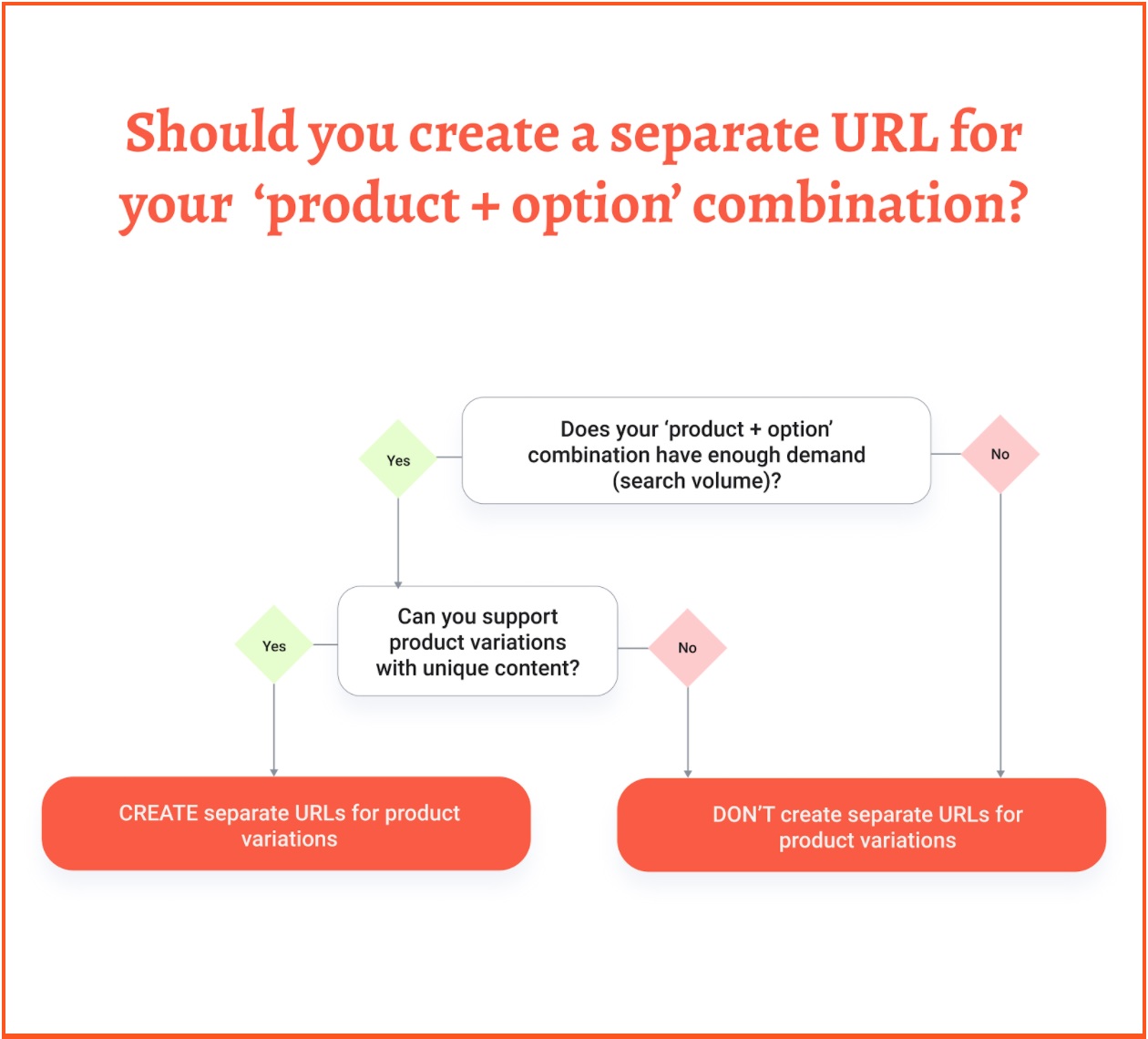
Unfortunately , there’s no one-size-fits-all approach here. Or, like SEOs say, ‘it depends’. First of all, you need to understand whether you need to have individual URLs for product variations or not. There are 2 things to consider here:
- Can these product variations pages stand on their own? Do they serve a particular purpose or just have 1-2 words changed compared to other variations of the same product?
- Do people search for the individual variations of the product? You can learn this by completing keyword research.
If the answer to at least one of these questions is ‘yes’, it’s better to leave the product variations pages having separate URLs. But it will also be valuable to add unique content to them.
If the answer is ‘no’ to one or both questions, Then there are 2 things you can do:
- Set up canonicals that will point to one product page. For example, to the Polka Dots Dress page.
- Unite all the pages into 1 and add colour swatches for people to choose the colours, sizes or other attributes they need.
3 ways to add unique content to the product variations pages
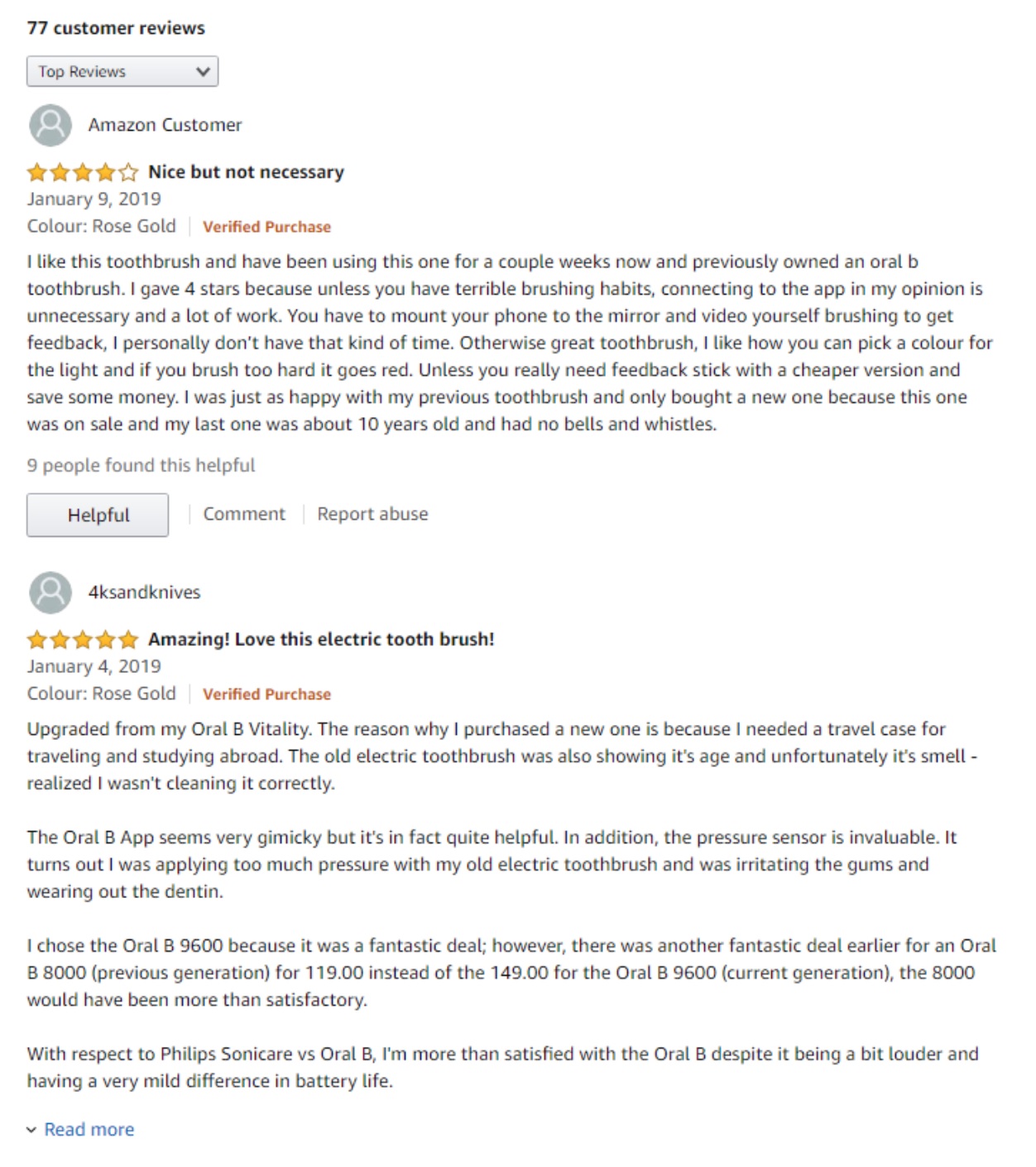
1.Customer Reviews
Reviews your customers leave on the product pages are a great source of unique content.
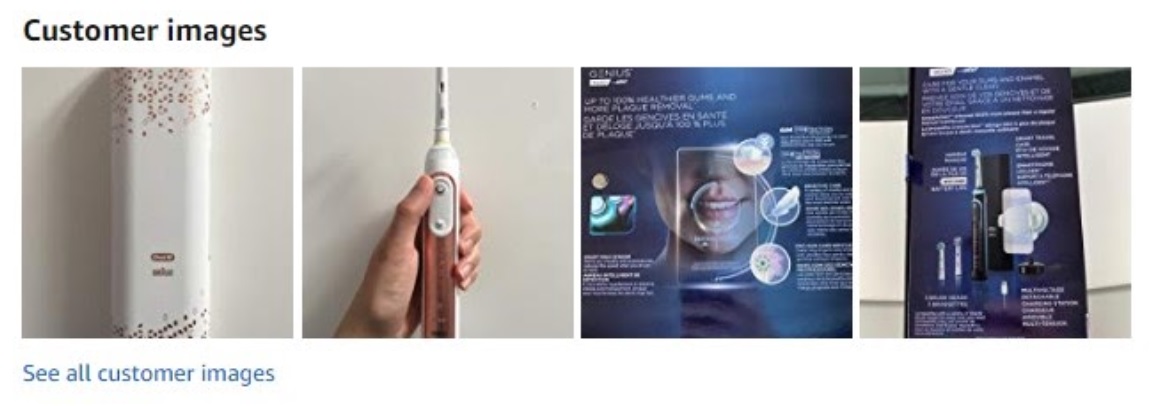
2. Customer Photos
Customer submitted photos also add to the uniqueness of the page. Moreover, they show your product in real life, which positively influences other buyers.
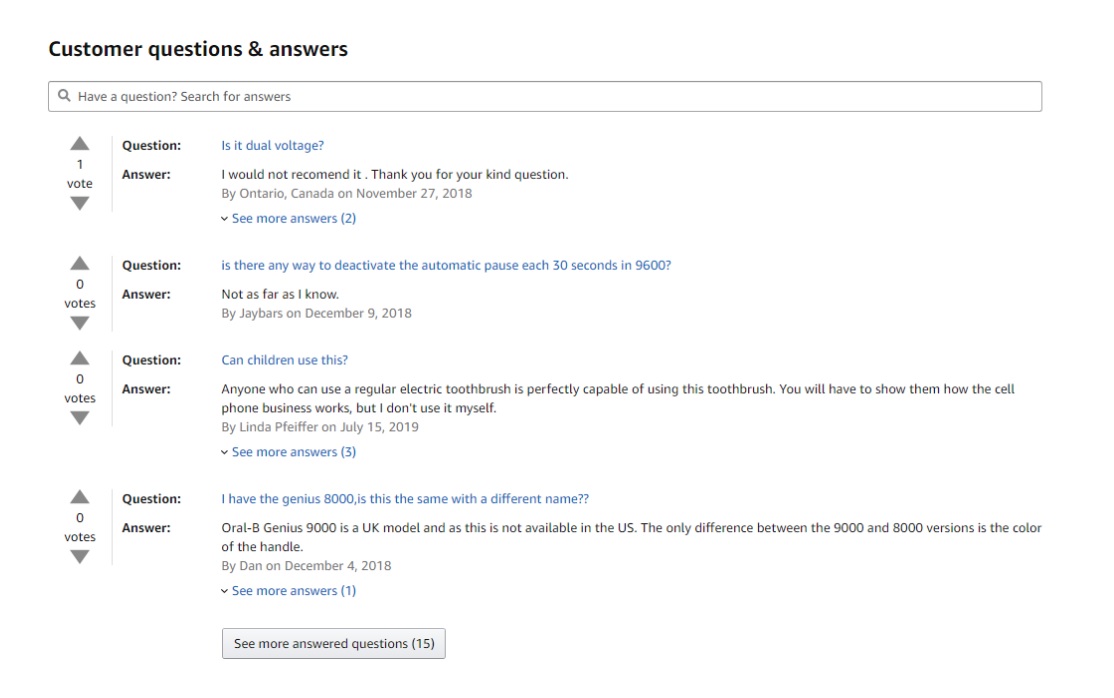
3. Questions and Answers sections
Sometimes people have questions before they commit to a purchase, which’s great; it shows they’re interested. Many times, they just don’t know where they should look for these answers, so having a QA section directly on the product page is a great way to give them all answers.
Such sections not only add unique content to the product variations pages, they also remove buying friction. It’s a win-win for you.
5. Create Content for Different User Search Intents
The main goal of any online store is to sell. But this doesn’t mean that each page should have an ‘add to cart’ button and convert people. A store also needs additional content to support the primary purpose.
Examples of such additional content are:
- Shipping/returns information
- Blog posts
- Knowledge base
- Buyer guides
- Etc
Why additional content is important ?
There are many reasons why additional content is essential, so we’ll use a list here too
- Additional content helps to improve brand awareness and capture top-funnel users (e.g. blog posts)
- It also helps to showcase your product to users who are in the consideration stage (e.g. buyer guides and how-to guides)
- Additional content helps you to increase loyalty and support existing customers as well (e.g. a knowledge base)
- Supporting content generates links much easier than commercial pages such as products or categories
- It helps you drive more traffic to your or your client’s store
- It creates an infrastructure that supports your money pages
- It helps you rank your website for the searches with non-commercial user intent
Here’s one more proof of the importance of additional content for an eCommerce website:
As you can see, creating additional content helps the overall online store goal to sell more.
What is user intent?
Answering this question helps online stores think about their CUSTOMERS, not about THEMSELVES. It is important.
Moreover, if you want to be on Google when people search for information, you’d need to have informational pages as products and categories URLs won’t rank for such types of searches.
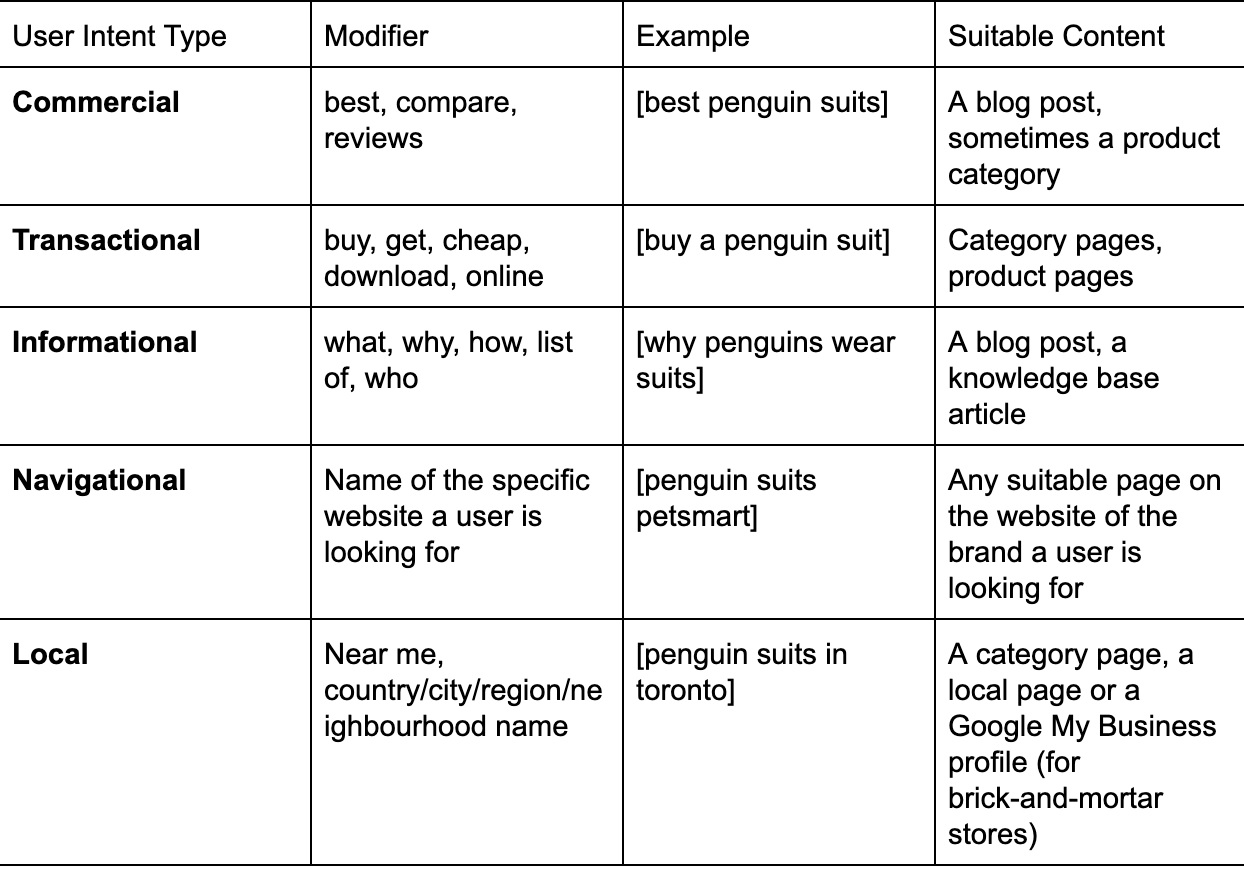
Types of user intent
There are generally 5 types of user intent recognized in marketing. it’s really important to think about theses as well when it comes to SEO:
You can use this approach and divide the searches into just 2 groups
In any case, understanding user intent is crucial for creating content and ranking it on Google or other search engines.
More facts about user intent
- User intent can be mixed – It means a search query can trigger both commercial and informational pages ranking for it.
- User intent is dynamic – User intent can change over time under particular circumstances, seasonality, important events or trends. For example, COVID has shifted user intent in many spheres from offline to online.
How to Optimize User Intent ?
Ok, now you know what the user intent is and understand its importance for successful SEO. Here’s an approach that will help you to use this knowledge in real life.
Step 1. Find the keywords to target
Create Specific Product Categories Instead of Broad Ones’ and created new categories targeting transactional user intent, you can concentrate on other intents here and get ideas for supporting content.
Step 2. Identify user intents of these keywords
There are a few ways to do it. First, you can look at the modifiers we shared in the table above. Secondly – look at the Google search results page for a particular query.
It will show you the types of content already ranking, and you’ll need to create the same type of content
This is a combination of transactional and local user intents. All the pages ranking here are category pages. It suggests that you’ll need to build a category page to rank for this search query.
Also, look at the additional features of the results page. Most transactional eCommerce searches will also show Google Shopping ads:
Here’s another example (which is very relevant for the work-from-home reality):
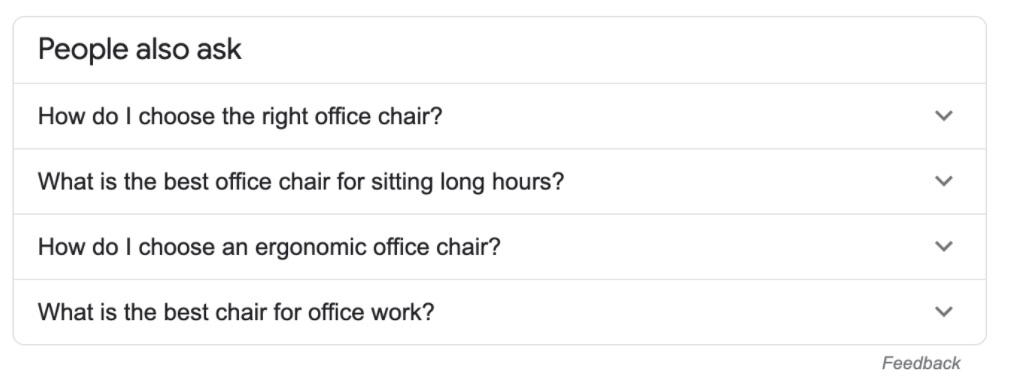
It’s informational user intent. And as you can see on the screenshot, the types of pages ranking for it are blog posts and guides. Also, note these Google search results features that suggest that the query has informational user intent:
A featured snippet
A ‘People also ask’ box
Step 3. Analyze 3-5 competitor pages
Before creating any content, you’ll need to understand how to stand out and be better than the pages already ranking for the keywords you’re going to target.
Things to look at:
- The amount of content on the page
- The title tags of the pages
- The H1-H6 headings
- Which sub-topics are covered
You don’t want to copy this. You want to use this information as guidance and be better.
Step 4. Create the content
Now when you have everything, go ahead and create supporting content.
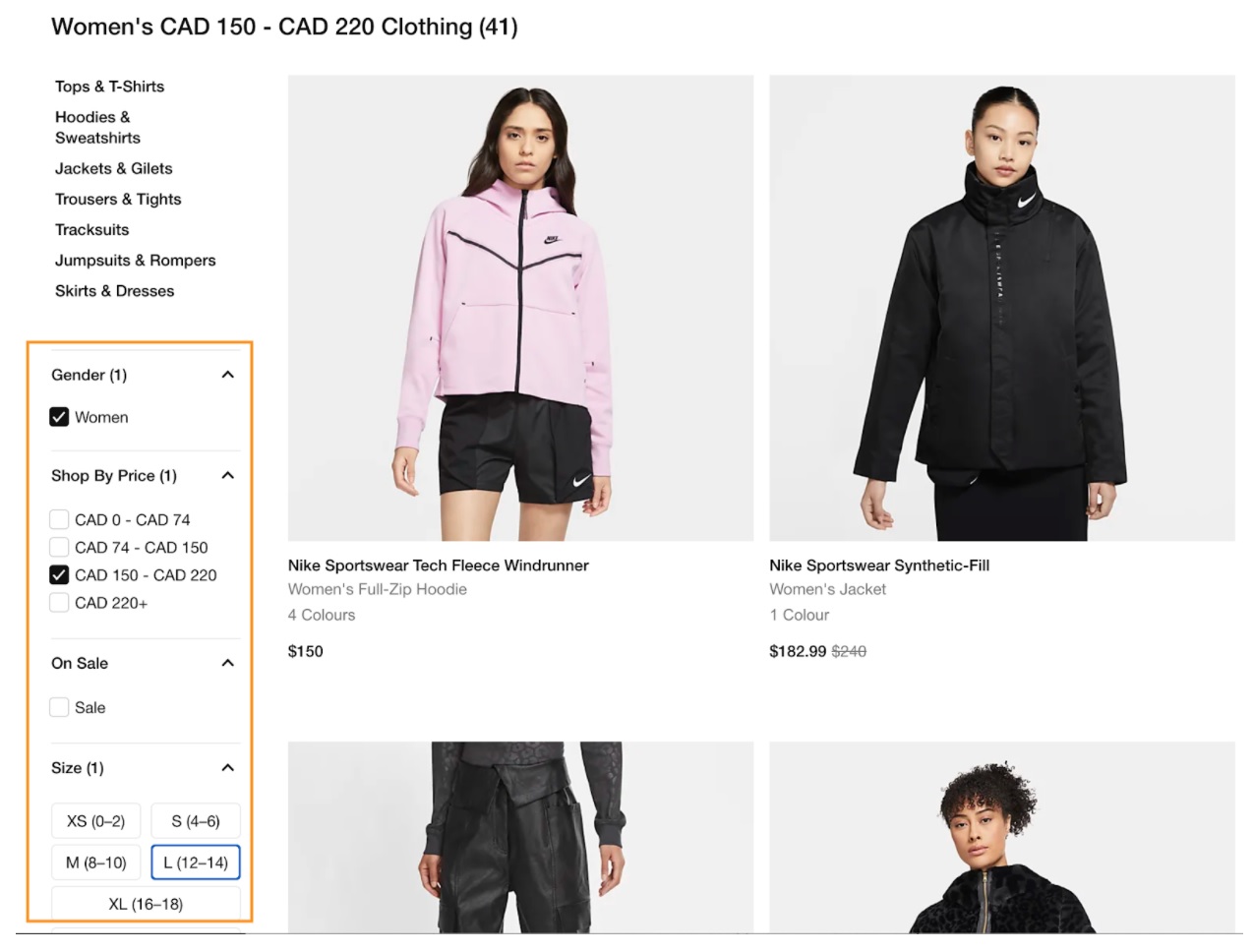
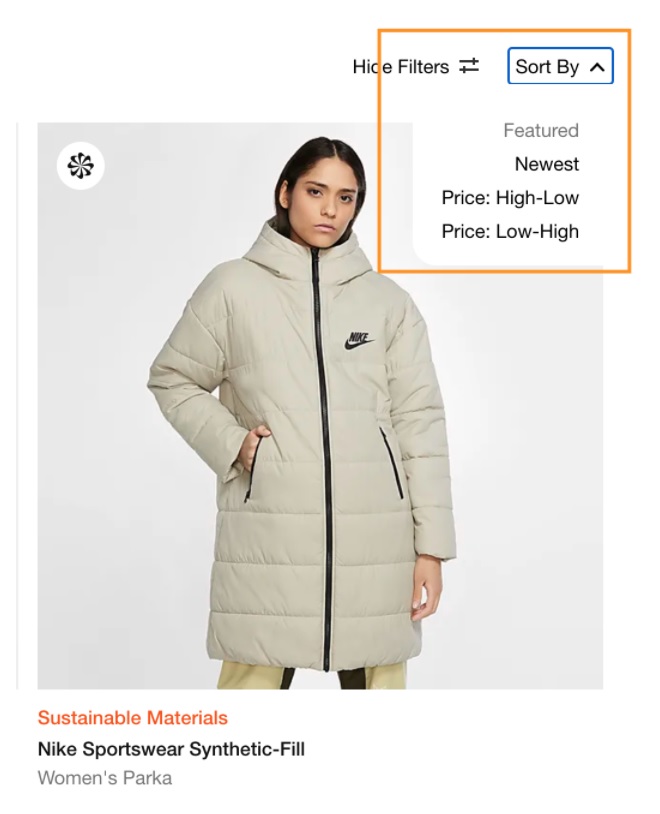
6. Make Faceted Navigation Work for You
Having filters and sorting options is excellent for user experience as they help drill down to specific products a customer wants.
Here’s an example of faceted navigation:
Here’s an example of sorting:
Though faceted navigation and sorting options are great, they also cause lots of SEO issues. The main problem is that they create new URLs that then get picked up and indexed by Google.
If you think about each and every filter combination, even in a small store, you will end up with thousands of URLs that are not valuable for Google as standalone landing URLs.
Example
Let say you have a category page for men t-shirts:
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts
But there’s also an option to sort the items on this page by price and bestsellers. So we end up with 2 new URLs:
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts?sort_by=price
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts?sort_by=bestsellers
Then one can also choose the colour and/or size. So you’ll have:
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts?filter=red
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts?filter=size=xl
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts?filter=red&size=xl
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts&size=xl&filter=red
These are 4 more new URLs. So we have 6 new URLs in total with just 2 sorting options and 2 filters. Usually, there are many more. That’s how faceted navigation creates SEO issues.
How to check the errors
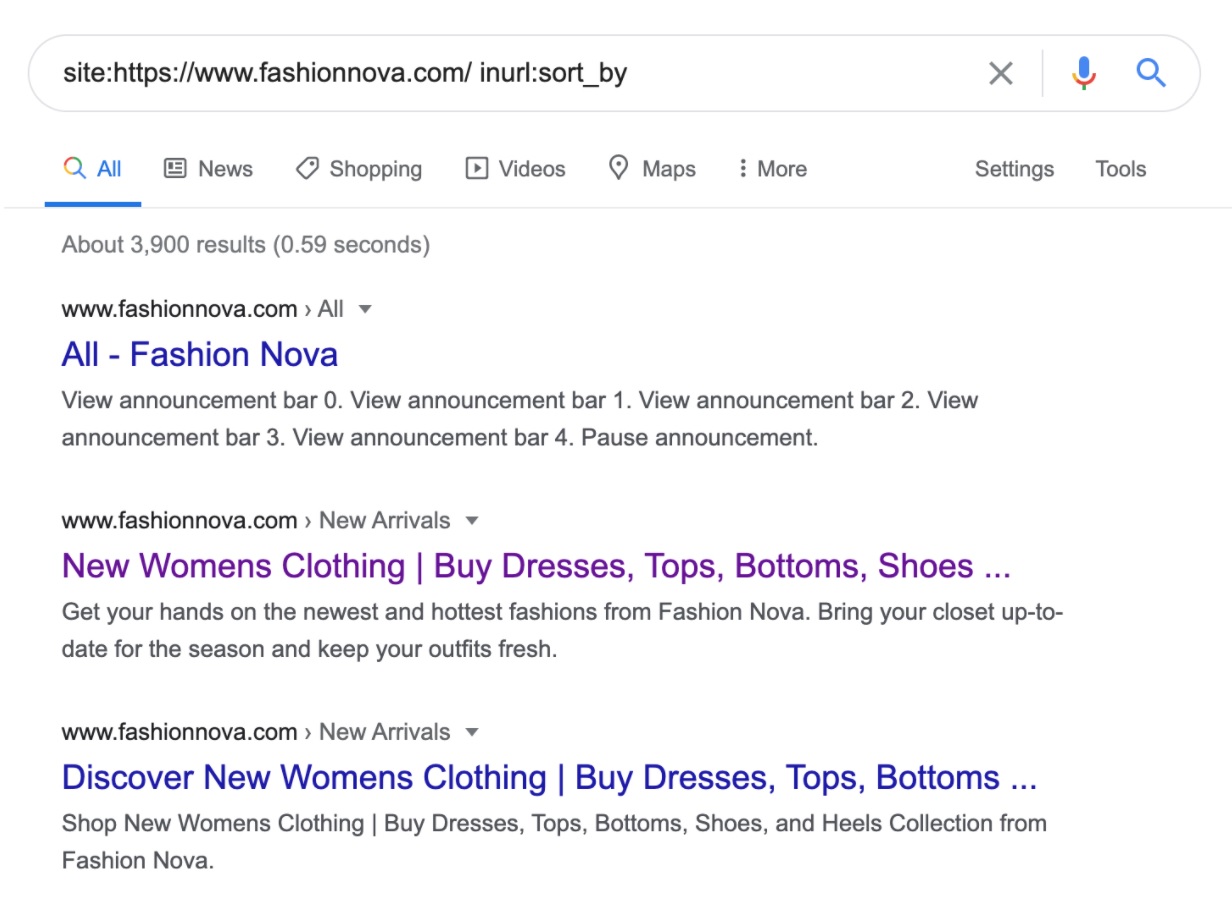
Here’s how you can check if an online store suffers from this issue. Go to the sorting page or filtering page and look at the parameter it uses. For example, ‘sort_by’. Then go to Google and search for: Site:store.com inurl:sort_by
Google will show all indexed pages from that domain that contain ‘sort_by’ in the URL. For example:
You will also find great insights in Google Search Console (look at the Coverage report and Crawl Insights)
Why Faceted Navigation is important ?
From Google’s perspective, all such pages look the same. The only difference is that the products are in a different order. But this doesn’t add any value. Moreover, the crawl budget suffers from having such pages as well.
How to Optimize Faceted Navigation ?
There are many approaches to handling faceted navigation. The one that we prefer is using canonical tags. The idea is to tell Google: only the main category URL should be treated as the preferred one, and all other variations should be ‘attached’ to it.
So that these URLs:
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts?filter=red
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts?filter=size=xl
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts?filter=red&size=xl
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts&size=xl&filter=red
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts?sort_by=price
- yourshop.com/men-t-shirts?sort_by=bestsellers
Have the following canonical tag: It’s a great solution used by many websites
- <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://yourshop.com/men-t-shirts” />
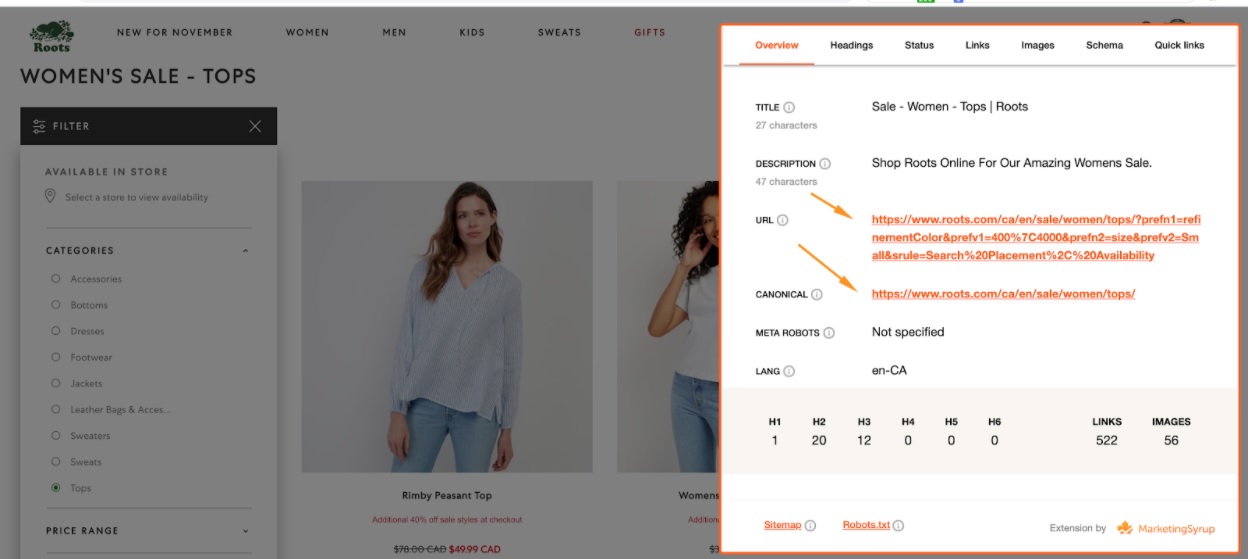
Here’s an example of Roots, a well-known Canadian apparel brand:
When we navigate to a category page with women tops and choose size and colour, the URL changes, but the canonical tag is pointing to the initial category URL.
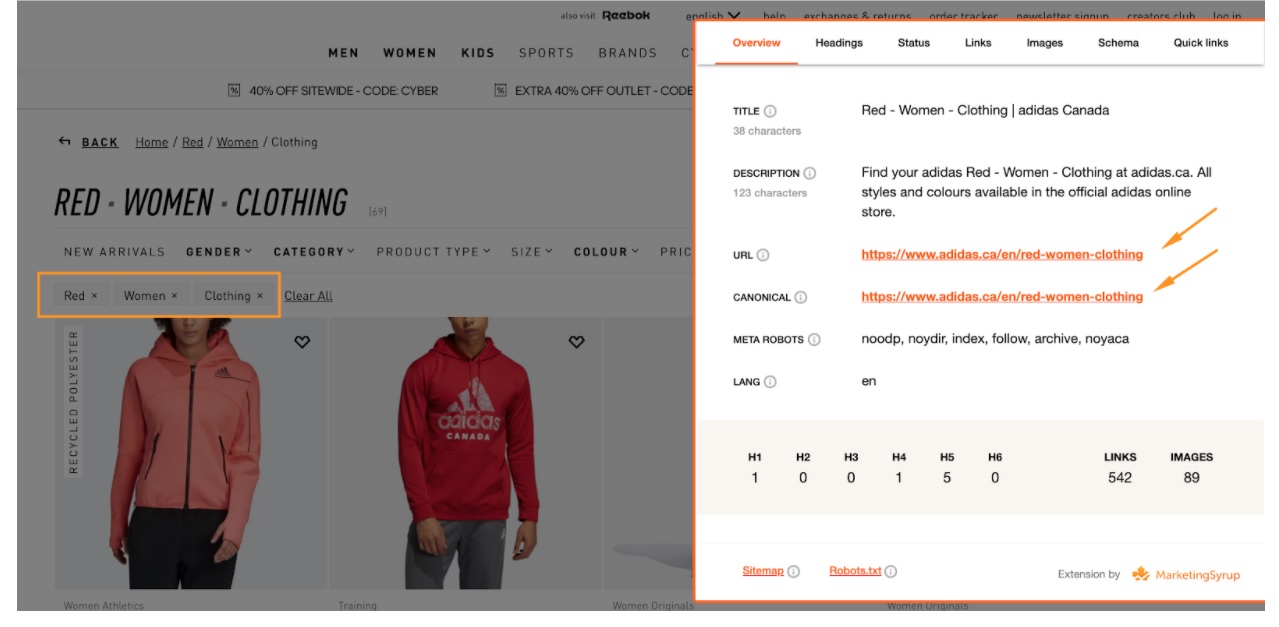
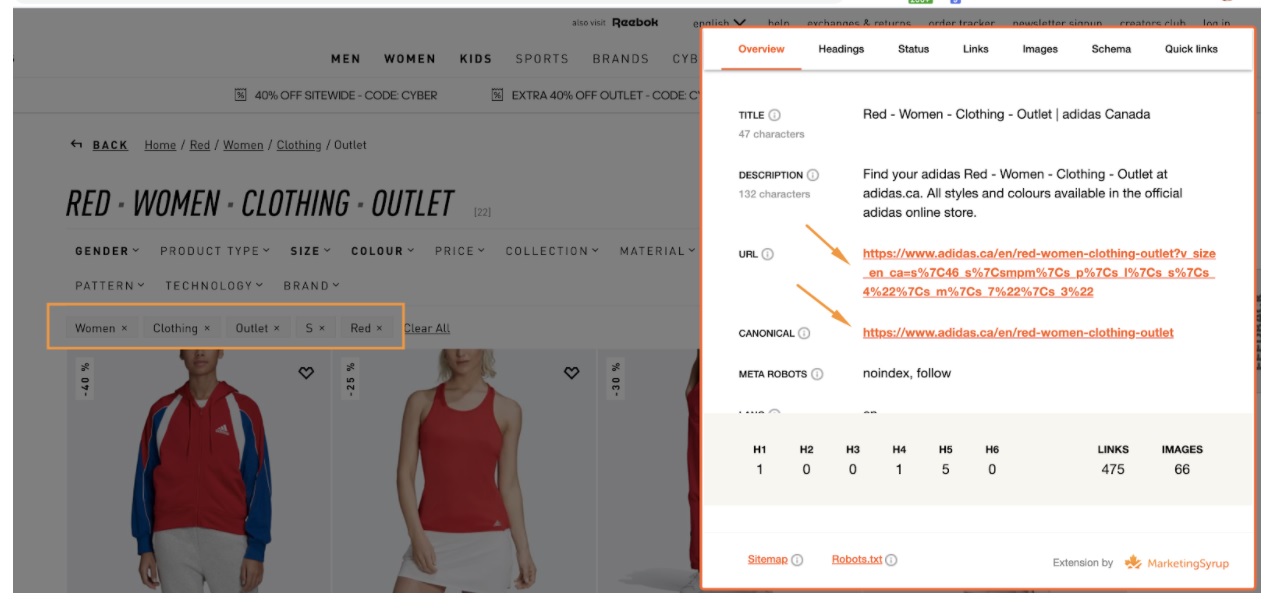
Here’s an example: Adidas uses a combination of facets that become separate pages and filters that add parameters to the category URLs. If I choose ‘clothing’, ‘women’ and ‘red’ as a colour, I’ll see a facet page with a clear URL and a self-referencing canonical tag:
This page will be ranking on Google and bring people to the website. If we choose ‘size’ in addition to the filters we’ve already selected, then URL parameters will be appended to the page URL:
Since the URL with parameters doesn’t have any additional value, it has a canonical pointing to the main facet page. The only downside of using canonicals to remove duplicate pages generated by faceted navigation is that Google still spends the crawl budget to go through the canonicalized URLs. It shouldn’t be an issue for you unless you have millions of pages.
Other options to Handle faceted navigation
- A noindex tag – You can add a noindex tag to the filtering and sorting pages so that Google discounts these pages altogether.
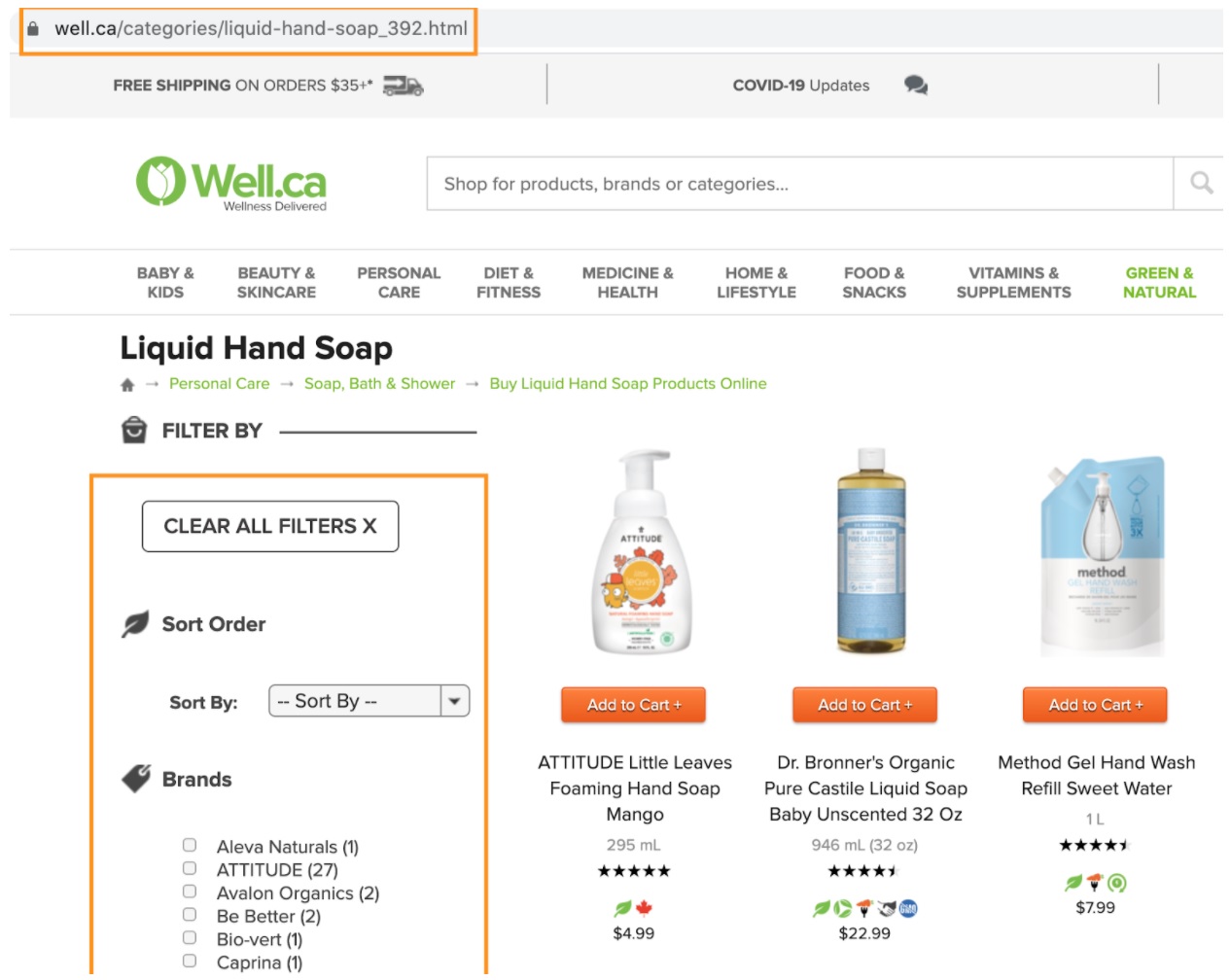
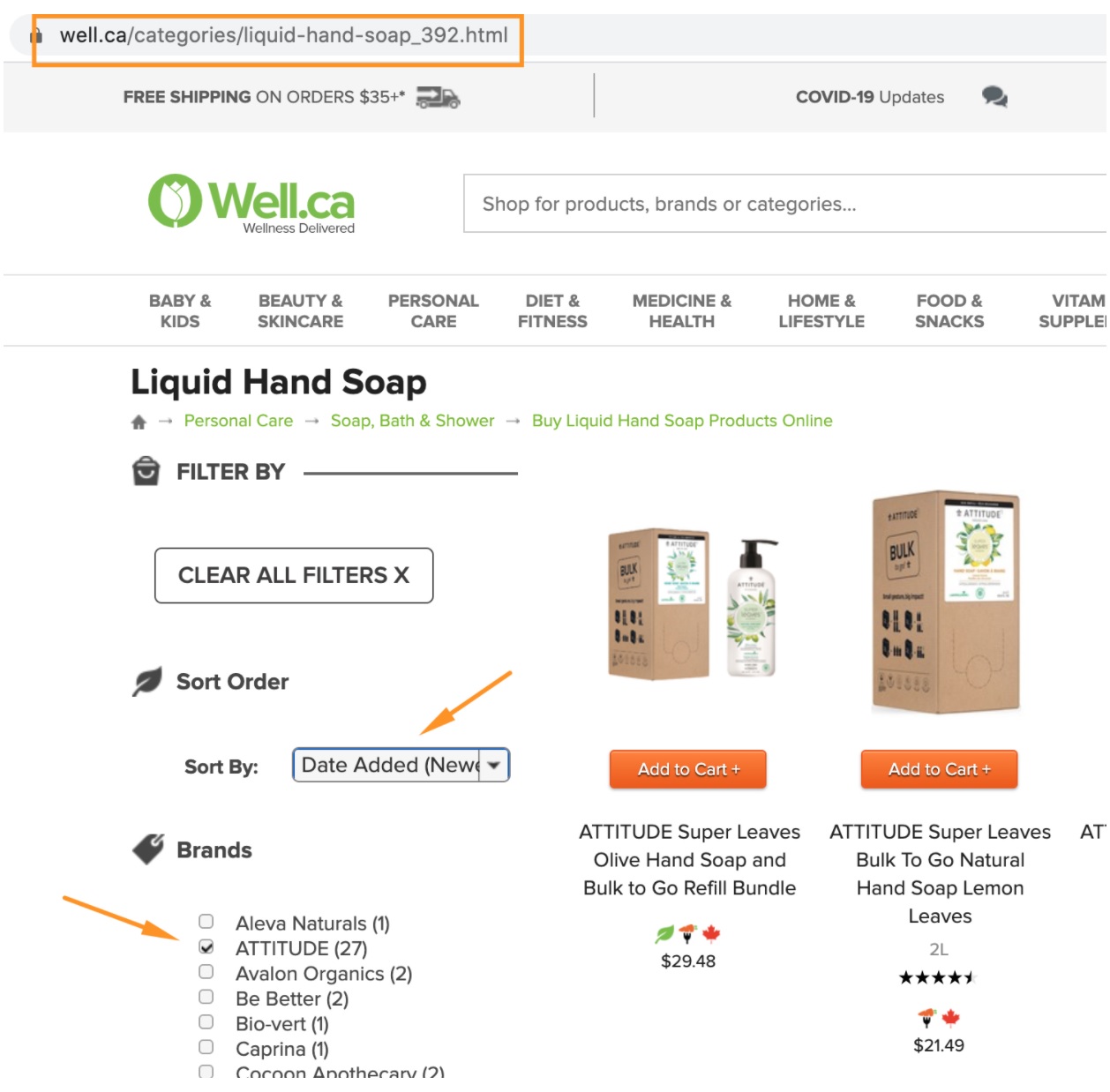
- AJAX filters – You can use AJAX to load filtered/sorted results. AJAX doesn’t create any new URLs, which means you won’t create duplicate pages in the first place.
Here’s an example of a category page with no filters applied:
And here’s the same page with a brand filter and a sorting option chosen:
As you can see, the category URL stays unchanged
7. Handle Discontinued and Sold out Products
It’s OK that some products come and go. Flexible stock is common for eCommerce-type websites. But it’s not always a good idea to remove a product page and serve a 404 error to anyone landing on it.
Why it’s important ?
First of all, user experience suffers when a potential customer lands on a ‘Not Found’ page. They most likely just leave your website and go to your competitors.
But there is more. Each existing page of your website acquires authority due to links (from your site and other sites out there) pointing to it. Pages need authority to rank.
Now think about that: every time you remove a page that has been around for some time, you just create a black hole where all the authority this page used to have disappears. Removing pages without a proper ‘recovery’ plan can cause significant traffic drops (sometimes they happen over time, sometimes, you notice them pretty quickly).
In the long run, your eCommerce website is becoming weaker. In a nutshell, old product pages returning 404s mean:
- Wasted money on attracting shoppers to the website
- Loss of potential revenue
- Decreasing brand loyalty
How to do it right ?
For temporarily out-of-stock products The aim is to turn a product page into a valuable asset.
Step 1: Leave the page as is (i.e. returning a 200 HTTP status code)
It will help the page to be indexed, crawled and visited by people as usual. But make sure to communicate properly that the product is out of stock. You can also enable backorders or back-in-stock subscriptions.
Step 2: Add alternative products to give options to the shoppers
While this particular product is out of stock, there can be similar items people might choose from. Add them to the page. By giving people a choice, you can get sales even if the product they initially wanted is currently unavailable.
Step 3: Remove the out-of-stock product from your promo blocks
It will help you direct customers’ attention in the right direction, i.e. to the products they can buy right now
Step 4: Once the product is back in stock, promote it
Add the product back to the promo blocks. Send notifications to those who subscribed for the back-in-stock alerts.
8. Improve Page Speed
Optimizing page speed is vital for conversions. And, of course, it’s also important for SEO. Here’s a summary of one study carried out by Shopify:
The numbers are enormous!
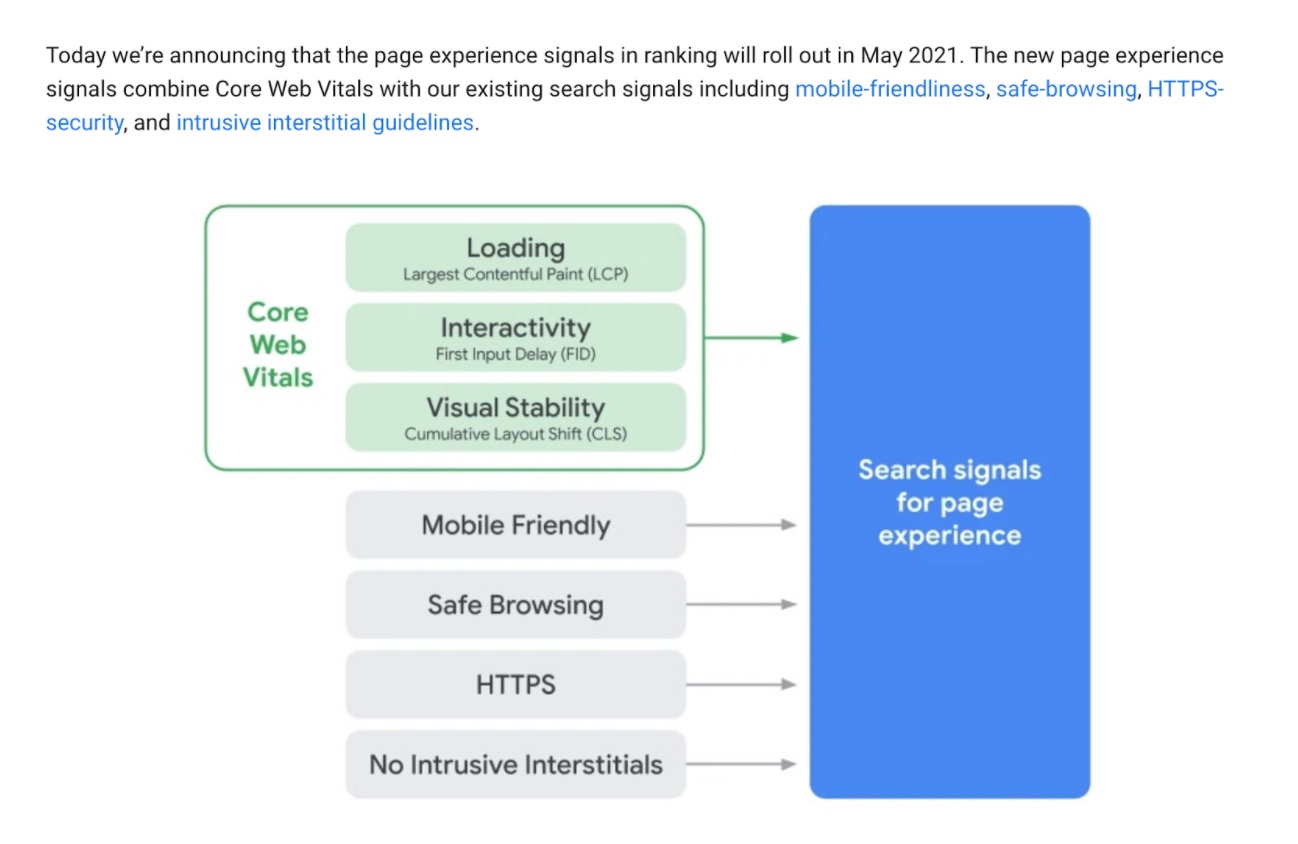
Google also considers page speed when ranking websites. Page speed has been named a ranking factor for a few years in the SEO industry, but in 2021 Google finally made this official by giving the exact date in 2021 when page speed will become more critical:
What this means is that page speed is now part of a landing page experience, and thus, it’s an official ranking factor (Google doesn’t always confirm ranking factor, so when it does, it’s important)
Page speed is now measured in the form of Core Web Vitals (announced in May 2021):
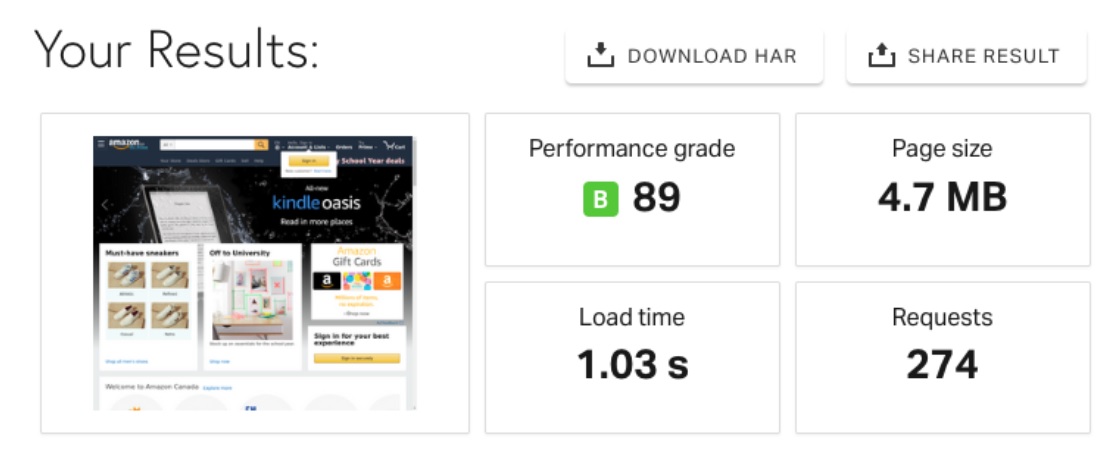
An average good eCommerce website should load in about 2 seconds (the faster, the better!). You can check here. For example, Amazon loads in 1 second!
How to Optimize Page Speed ?
Optimizing page speed is not an easy task, and you might need the developer’s help to do it. But still, there are easy things (like image optimization) you can easily do yourself. we will give you the process that will help you improve page speed in your or your client’s online store.
- Analyze the current page speed
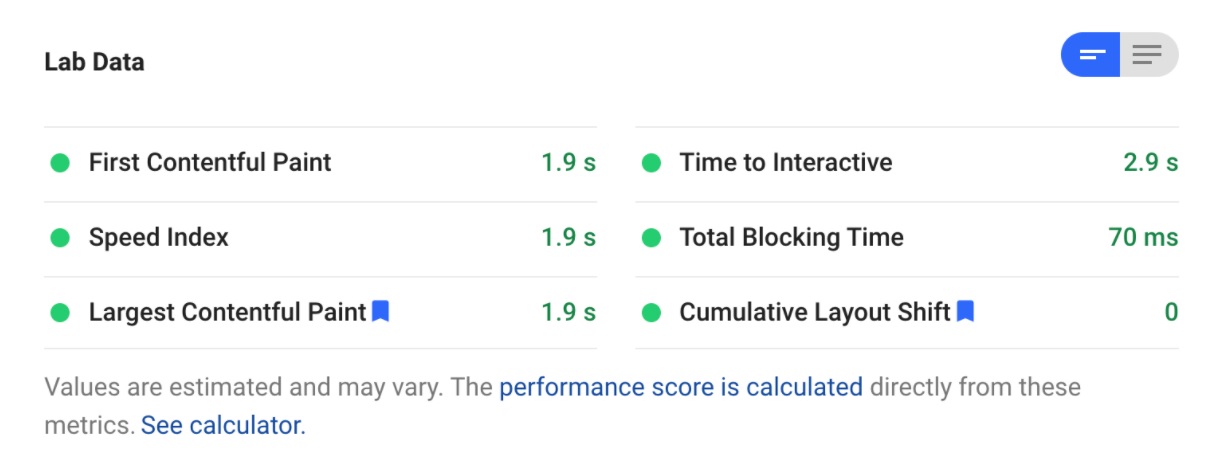
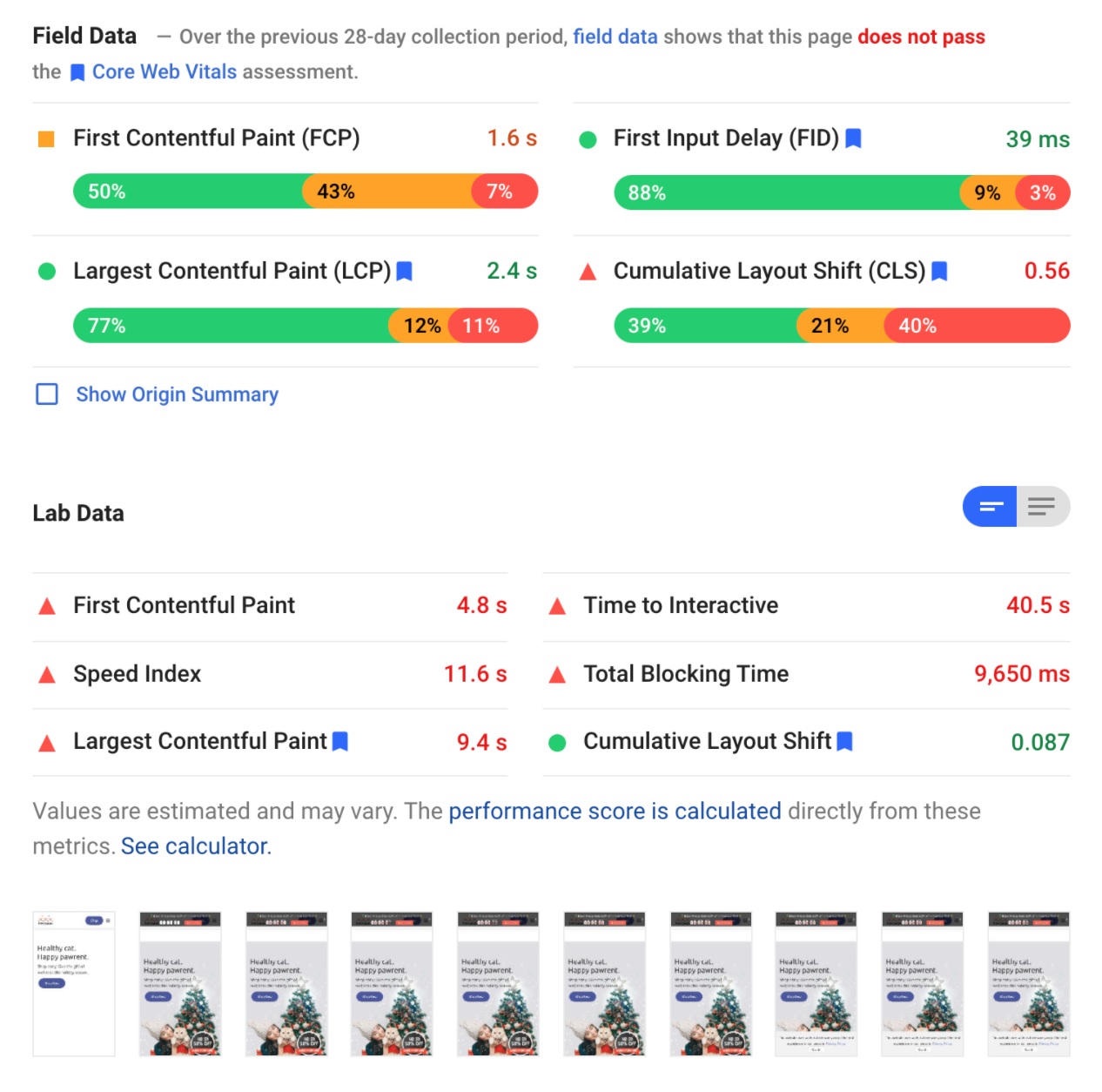
PageSpeed Insights tool You can use the to get your core Web Vitals numbers right from Google:
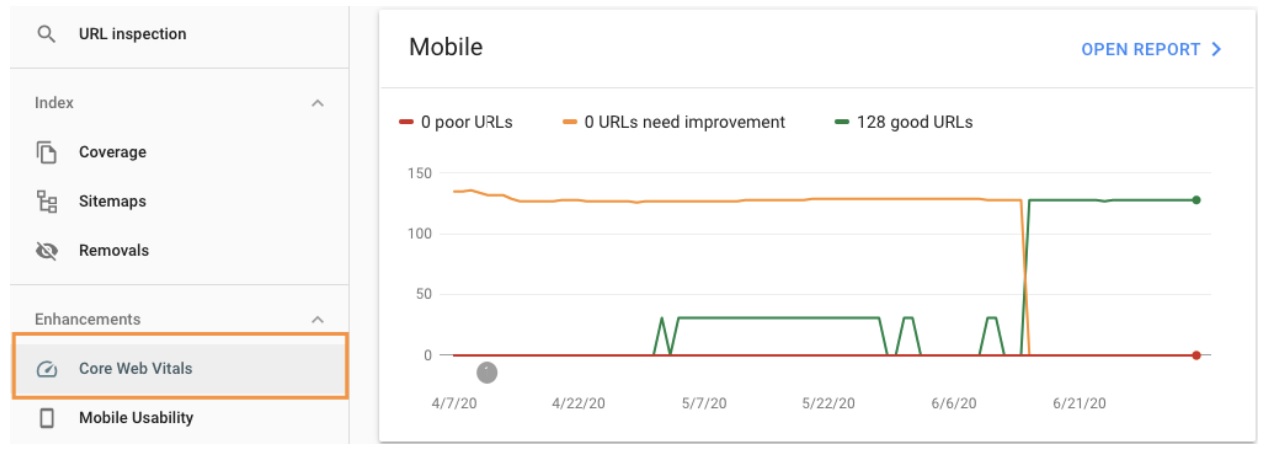
Plus, there’s a dedicated report you can find in your Google Search Console under ‘Core Web Vitals’:
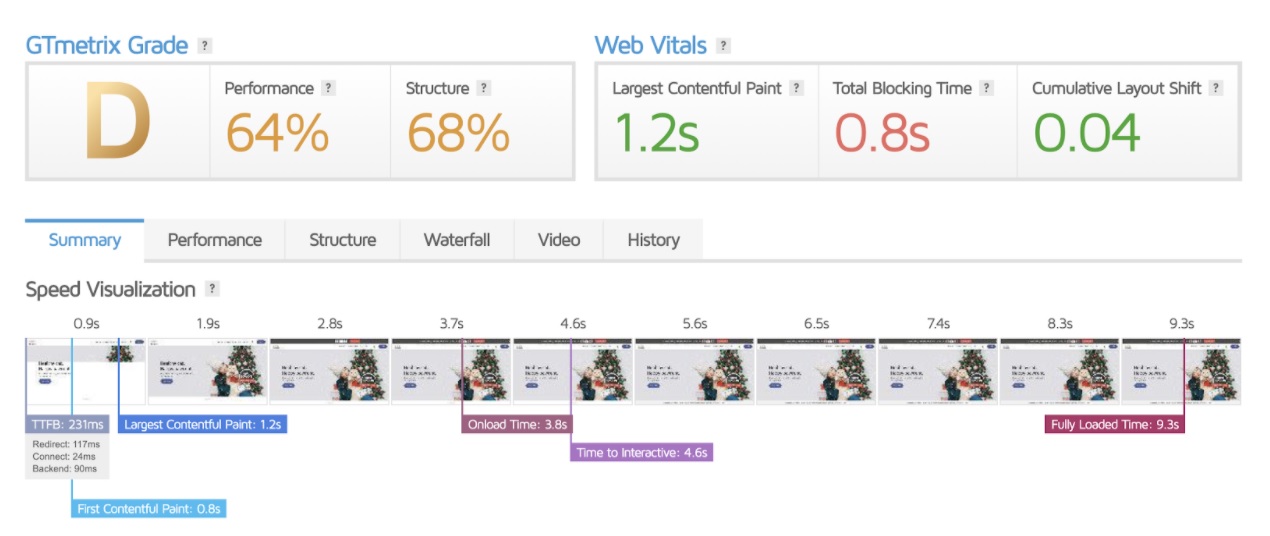
Another tool that you can use is gtmetrix . It has been recently updated to show Core Web Vitals as well. Here’s an example of one website:
And here’s the same website checked in Google PageSpeed Insights
we find that the results in the Google PageSpeed Insights tool usually show worse scores than GTmetrix. you can trust Google’s tool more but using a combination of sources can help you see things from different angles. Moreover, each tool gives suggestions for speed improvement.
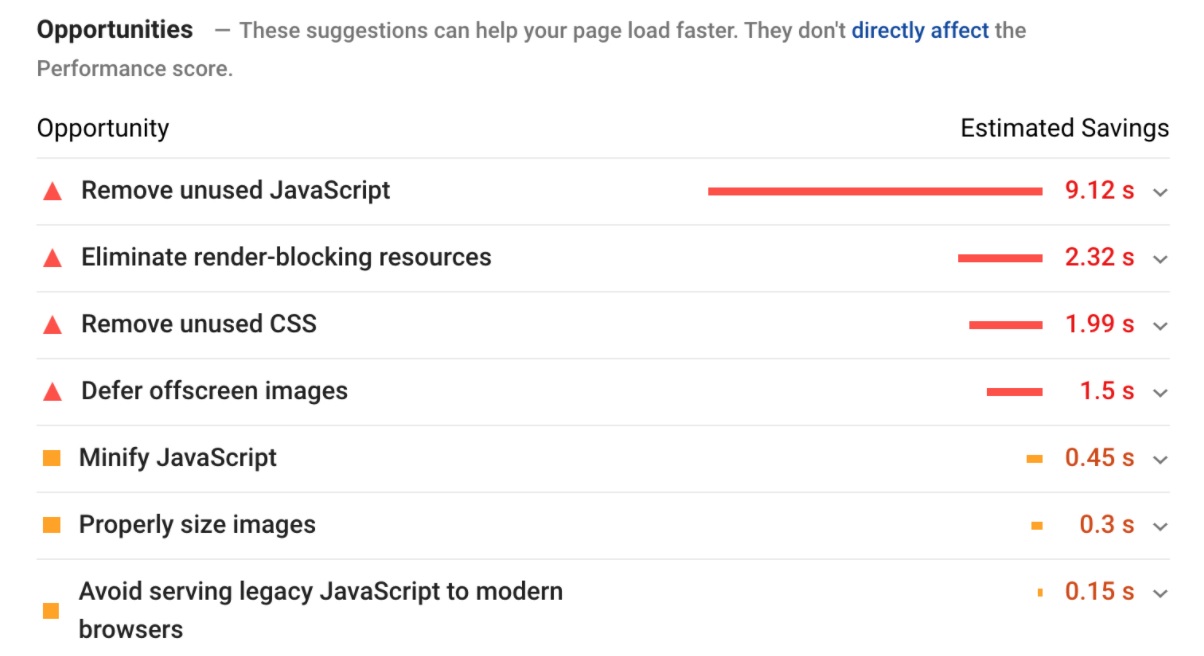
- Analyze suggestions for speed improvement
The tools we showed you above will give you suggestions. Here’s GTmetrix:
And here are the suggestions from PageSpeed Insights:
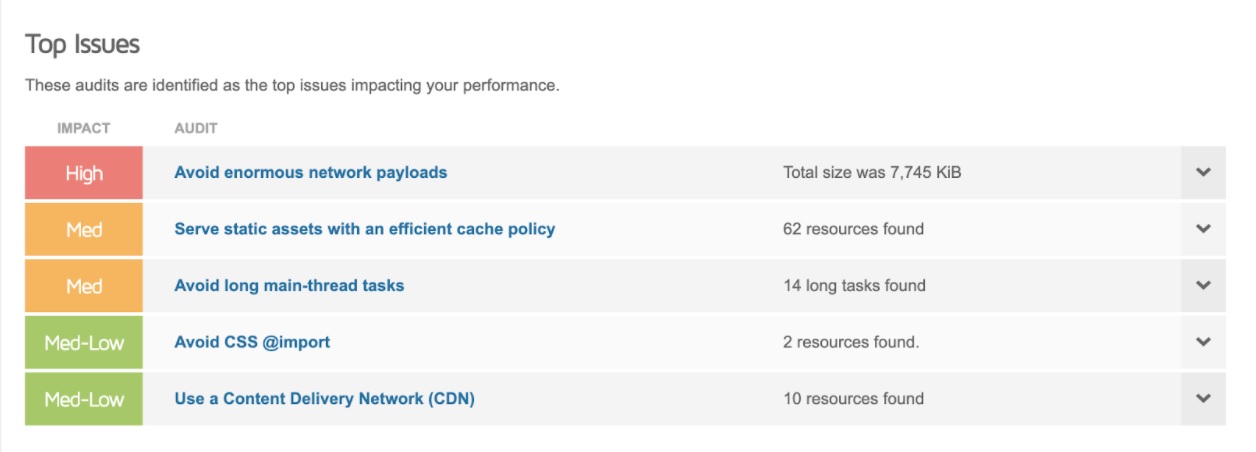
If you go through these reports, you’ll find common issues and examples of the file URLs causing delays in loading your page.
- Remove 3-rd party scripts you no longer need
Built with Some marketing person installed some 3rd-party script, then forgot to remove it, and 3 years later, it’s still on the website doing nothing but slowing down page load times. It happens a lot, especially with big teams.
Another example is leaving the script that you needed temporarily, e.g. HotJar. You tested user behaviour, you changed the interface according to this, the sales increased. Cool. But then the HotJar code is hanging out there though you never checked user behaviour through it again.
That’s why finding a revision of 3rd-party scripts an important step that needs to be done regularly. First of all, you’ll find the scripts after completing Step 2 above. Additionally, use builtwith It has a more user-friendly way of presenting these scripts. This tool was not designed for page speed optimization, but try it.
Here’s an example of how it looks like:
Go through all widgets, 3-rd party tools and make a list of those along with suggested action (e.g. remove/keep/pause). You will then need to talk to the person in your company or your client’s team who can give you more insights into which 3-rd party tools are necessary for the online store.
It can be a marketing manager if you’re helping the online store as a consultant. Or it can be yourself if you own the store (it’s always great to talk to a smart person, isn’t it?).
- Optimize images
1. Use the images of the actual size or a little bigger than you need
Let’s say you need a product image of 300x300px. You can upload a 300x300px pic or even 500x500px, it will work as well. But don’t upload a 4000x4000px pic as it will ‘steal’ the loading time.
Think about that: there are 10 product images on a page, and each of them is loaded on a page load. If all of them are much bigger than needed (4000x4000px vs 300x300px as in the example above), you’re asking too much from your user’s browsers.
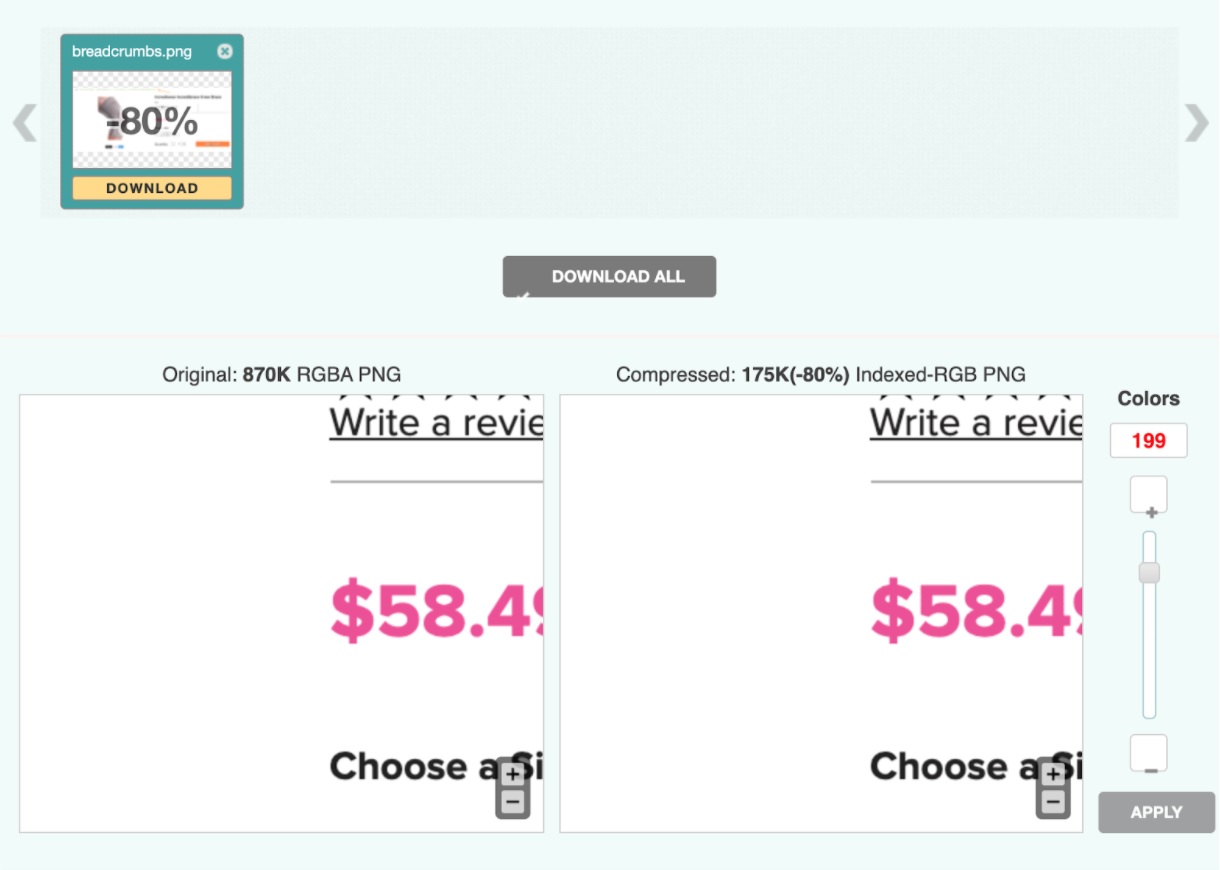
2. Compress images
Compressing images helps them ‘shake off’ some weight, which means they will load even faster. Every eCommerce platform has extensions and plugins to do that. If you want to do it manually, we’d recommend imagecompressor
.
Here’s an example of how an image can go from 870k to 175k – which is an 80% reduction – without any loss in the image quality:
- Minify JS and CSS files
Minification is a process of removing unneeded parts from the files with code such as blank lines. Doing so with your CSS and JS files will help you improve page speed.
Note, this is not something you need to do manually. Every eCommerce platform can either have this feature out-of-the-box, or there’s a plugin for that.
9. Make Your Pagination Crawlable
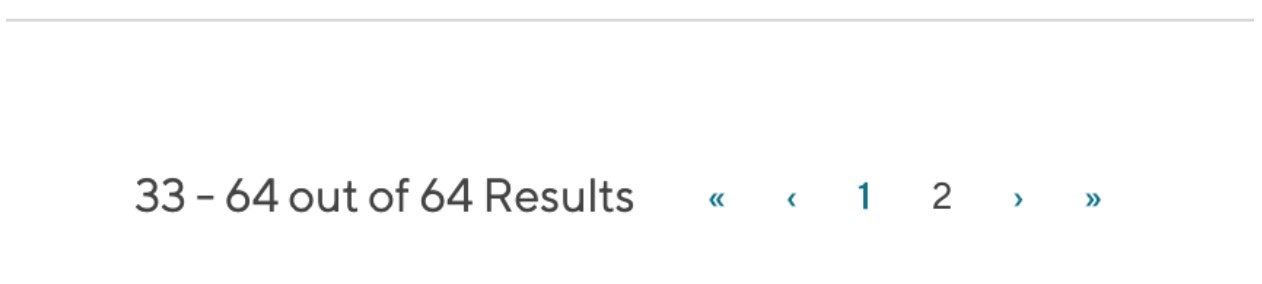
We all have seen these numbers on the category pages in any eCommerce website:
If you have many products that don’t fit in on 1 page, you have multiple pages. It’s easy. The confusion arises when people think that these paginated URLs (page-2, page-3, page-4, etc.) are duplicate or thin content. And as a result, they:
- Either noindex these paginated URLs
- Or set up the canonical tags to point to the main category page (basically, page-1 in this pagination URLs series)
In this example, page 2 is canonicalized to the main category page (which is the first page).
The problem with canonicalizing all the URLs in a paginated sequence to the first page is that you “cut off” Page 2, Page 3, Page N. They might just as well not exist to Google. And this is not the best decision, especially if you have many products or a dynamic stock (like many online stores).
Why Pagination is important ?
In reality, the paginated URLs are not duplicates, so Google crawling and indexing them is not an issue.
Moreover, they perform an essential task for you – support a healthy internal linking structure so that Google can follow all the internal links found on them, index/reindex products and properly see the relations between the internal pages.
How to Optimize Pagination URL’s ?
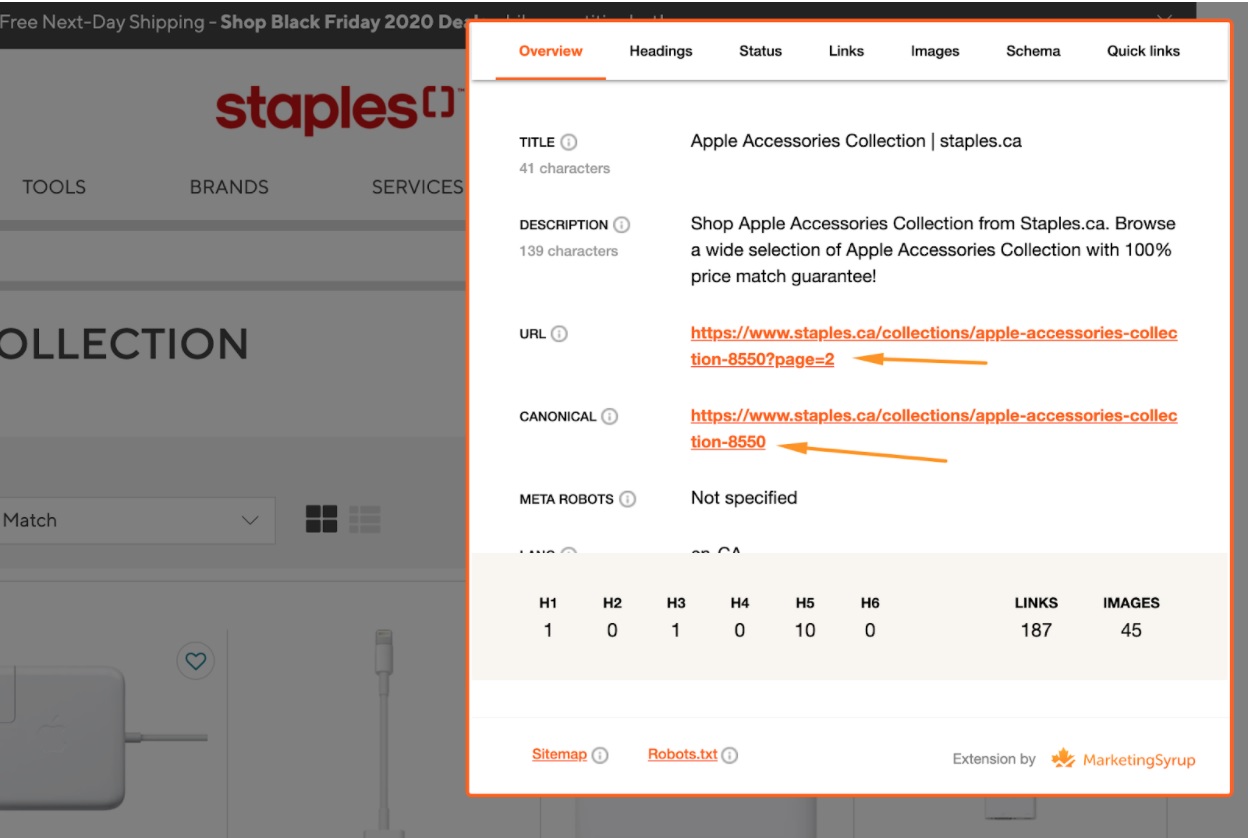
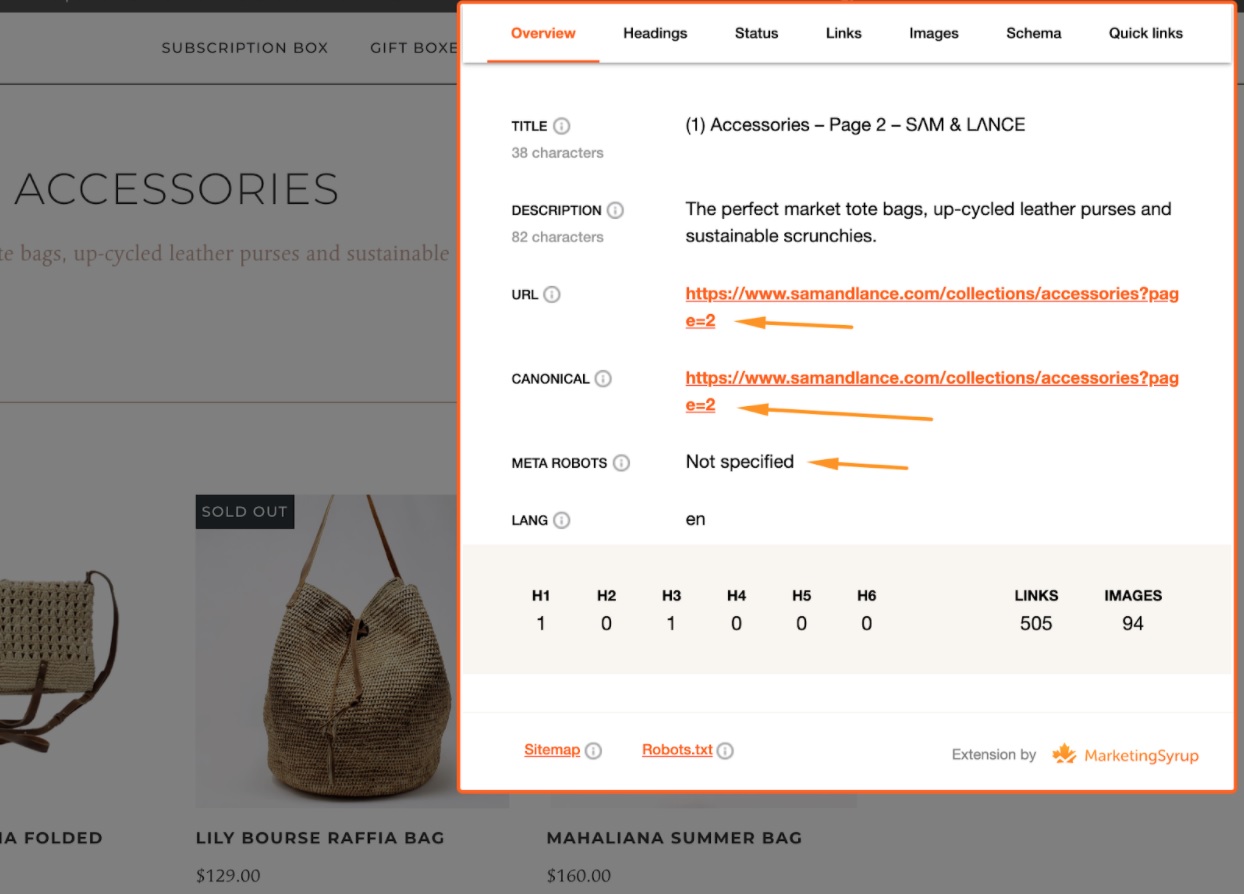
You need to make sure that all paginated URLs have:
- The meta robots tag is set to ‘index,follow’ or just empty. Both these approaches mean that the indexing of a page is allowed and that Google can follow the links found on the page – that’s exactly what we need.
- The paginated URL has a canonical pointing to itself (i.e. a self-referencing canonical) or an empty canonical (not recommended but possible)
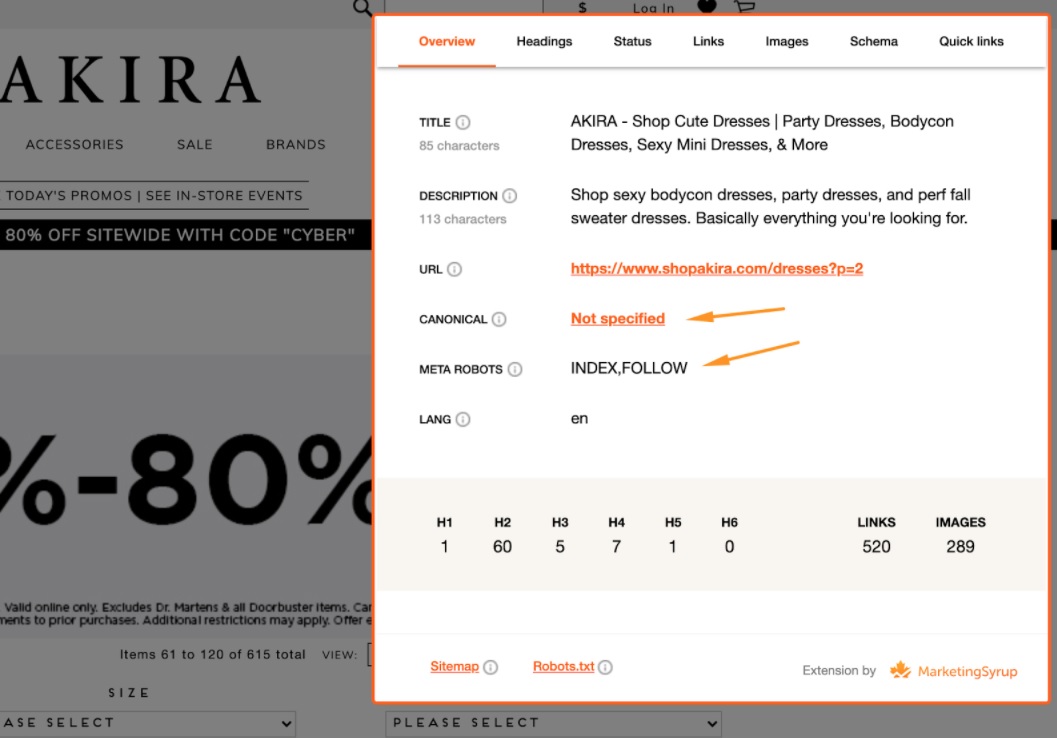
- The canonical is not specified
- The meta robots tag is set to ‘index,follow’
- The canonical tag points to the page URL
- The meta robots tag is not specified
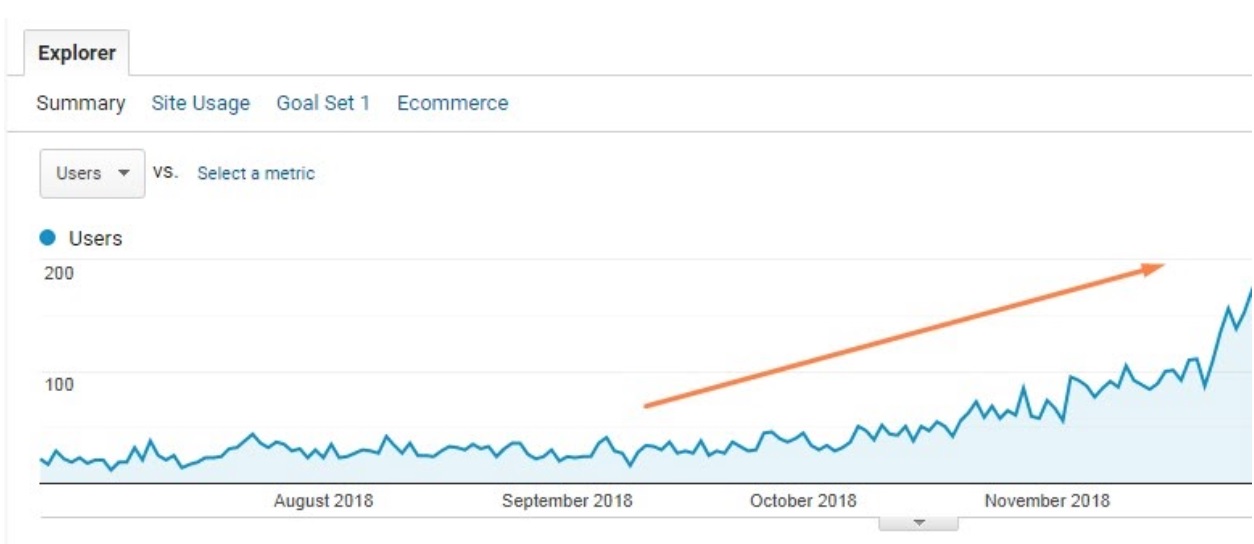
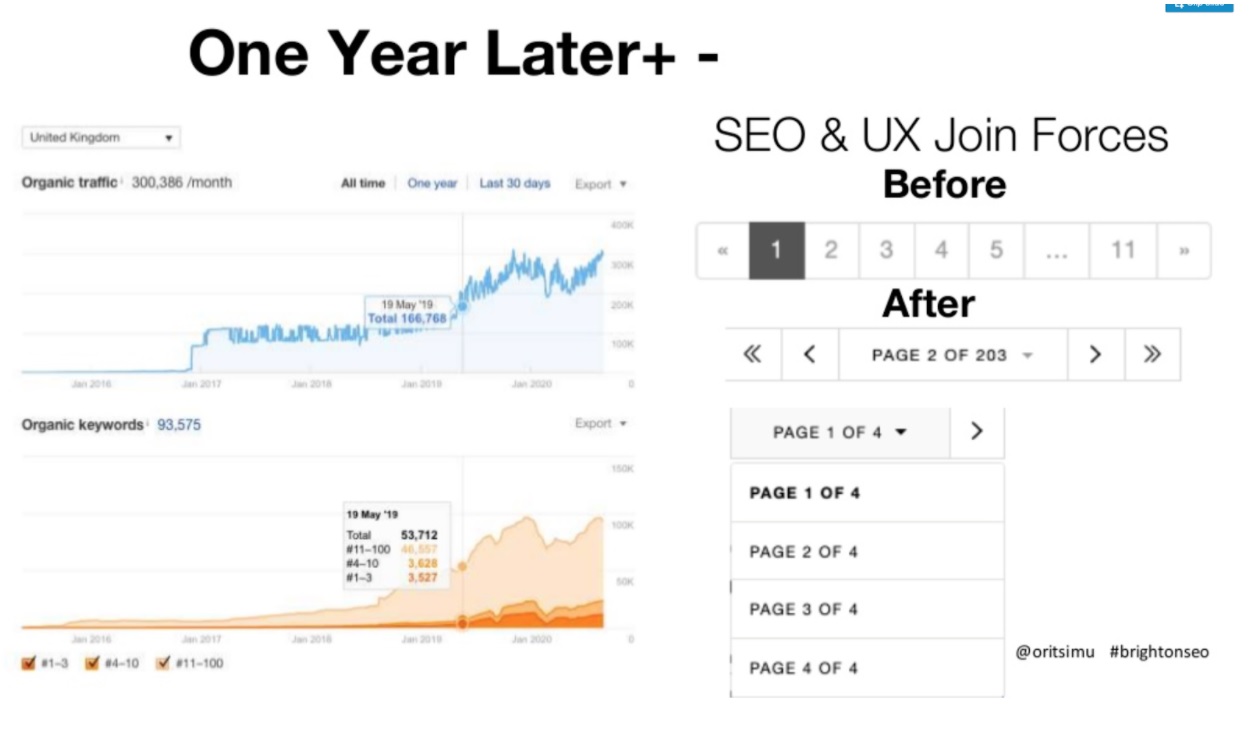
Real-life example
This store used to have non-indexable and not crawlable pagination. This is what happened when they set up the navigation the right way:
The traffic has dramatically increased! as it illustrates the right SEO-friendly approach to pagination in online stores. You can find the original deck by Orit here.
Check more Interesting Articles:
How To Find Suppliers For Ecommerce Store
Why Shopify Is The Best Ecommerce Solution
Top 6 Success Ecommerce Strategies For Small Busines
How To Write Perfect Product Descriptions For ECommerce Store
8 Actionable ECommerce Marketing Tactics To Drive More Sales
Conclusion
when you are starting out ecommerce seo, you concentrated on fixing any issues one by one. It worked in the short term. But in the long run, this approach prevented from seeing the forest for the trees. The truth is there are 2 main reasons why most SEO issues happen:
- Thre’s no process to handle them
- The process is broken
Instead of chasing every issue separately, create a process that will do it for you in a more efficient way.
Consider Following a Course ?
With Lifetime Access ?
We have been the number 1# platform for delivering most demanding course. Becoming Lifetime Member , You will receive all the Premium content For FREE

Consider Following a Course ? With Lifetime Access ?
We have been the number 1# platform for delivering most demanding course. Becoming Lifetime Member , You will receive all the Premium content For FREE